Targeting Microglial Metabolic Rewiring Synergizes with Immune-Checkpoint Blockade Therapy for Glioblastoma
- PMID: 36649564
- PMCID: PMC10073346
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0455
Targeting Microglial Metabolic Rewiring Synergizes with Immune-Checkpoint Blockade Therapy for Glioblastoma
Abstract
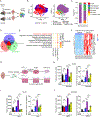
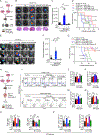
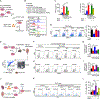
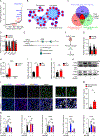
Glioblastoma (GBM) constitutes the most lethal primary brain tumor for which immunotherapy has provided limited benefit. The unique brain immune landscape is reflected in a complex tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) in GBM. Here, single-cell sequencing of the GBM TIME revealed that microglia were under severe oxidative stress, which induced nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2 (NR4A2)-dependent transcriptional activity in microglia. Heterozygous Nr4a2 (Nr4a2+/-) or CX3CR1+ myeloid cell-specific Nr4a2 (Nr4a2fl/flCx3cr1Cre) genetic targeting reshaped microglia plasticity in vivo by reducing alternatively activated microglia and enhancing antigen presentation capacity for CD8+ T cells in GBM. In microglia, NR4A2 activated squalene monooxygenase (SQLE) to dysregulate cholesterol homeostasis. Pharmacologic NR4A2 inhibition attenuated the protumorigenic TIME, and targeting the NR4A2 or SQLE enhanced the therapeutic efficacy of immune-checkpoint blockade in vivo. Collectively, oxidative stress promotes tumor growth through NR4A2-SQLE activity in microglia, informing novel immune therapy paradigms in brain cancer.
Significance: Metabolic reprogramming of microglia in GBM informs synergistic vulnerabilities for immune-checkpoint blockade therapy in this immunologically cold brain tumor. This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 799.
©2023 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: No conflict of interest is declared.
Figures


References
-
- Weller M, Wick W, Aldape K, Brada M, Berger M, Pfister SM, et al. Glioma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015;1:15017. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, Van-Den-Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 2009;10:459–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

