An antisense amido-bridged nucleic acid gapmer oligonucleotide targeting SRRM4 alters REST splicing and exhibits anti-tumor effects in small cell lung cancer and prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 36650528
- PMCID: PMC9847160
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02842-1
An antisense amido-bridged nucleic acid gapmer oligonucleotide targeting SRRM4 alters REST splicing and exhibits anti-tumor effects in small cell lung cancer and prostate cancer cells
Abstract
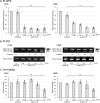
Background: Antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) medicine for clinical applications has been becoming a reality. We previously developed a gapmer ASO targeting Ser/Arg repetitive matrix 4 (SRRM4) that is abnormally expressed in small cell lung cancer (SCLC). However the detailed mechanism of ASO through repressing SRRM4 has not been completely elucidated. Further, effectiveness of SRRM4 ASO to prostate cancer (PCa) cells expressing SRRM4 similar to SCLC remains to be elucidated. RE1-silencing transcription factor (REST) is a tumor suppressor, and its splicing isoform (sREST) is abnormally expressed by SRRM4 and causes carcinogenesis with neuroendocrine phenotype in SCLC. The present study aimed to understand the contribution of REST splicing by SRRM4 ASO administration.
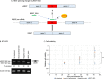
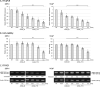
Methods: SRRM4 expression and REST splicing were analyzed by RT-qPCR and conventional RT-PCR after treating SRRM4 ASO, and cell viability was analyzed in vitro. Exogenous reconstitution of Flag-tagged REST plasmid in SCLC cells and the splice-switching oligonucleotide (SSO) specific for REST was analyzed for cell viability. Furthermore, we expanded the application of SRRM4 ASO in PCa cells abnormally expressing SRRM4 mRNA in vitro.
Results: SRRM4 ASO successfully downregulated SRRM4 expression, followed by repressed cell viability of SCLC and PCa cells in a dose-dependent manner. Administration of SRRM4 ASO then modified the alternative splicing of REST, resulting reduced cell viability. REST SSO specifically modified REST splicing increased REST expression, resulting in reduced cell viability.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that a gapmer ASO targeting SRRM4 (SRRM4 ASO) reduces cell viability through splicing changes of REST, followed by affecting REST-controlled genes in recalcitrant tumors SCLC and PCa cells.
Keywords: Antisense oligonucleotide; Gapmer; Prostate cancer; REST/NRSF; SCLC; SRRM4; Small cell lung cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Setoguchi K, Cui L, Hachisuka N, Obchoei S, Shinkai K, Hyodo F, Kato K, Wada F, Yamamoto T, Harada-Shiba M, et al. Antisense oligonucleotides targeting Y-Box binding protein-1 inhibit tumor angiogenesis by downregulating Bcl-xL-VEGFR2/-Tie axes. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;9:170–181. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.09.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

