Identification of Natural Products Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 by Targeting Viral Proteases: A Combined in Silico and in Vitro Approach
- PMID: 36651644
- PMCID: PMC9885530
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00843
Identification of Natural Products Inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 by Targeting Viral Proteases: A Combined in Silico and in Vitro Approach
Abstract
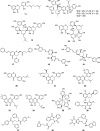
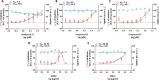
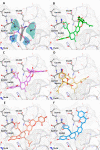
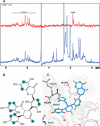
In this study, an integrated in silico-in vitro approach was employed to discover natural products (NPs) active against SARS-CoV-2. The two SARS-CoV-2 viral proteases, i.e., main protease (Mpro) and papain-like protease (PLpro), were selected as targets for the in silico study. Virtual hits were obtained by docking more than 140,000 NPs and NP derivatives available in-house and from commercial sources, and 38 virtual hits were experimentally validated in vitro using two enzyme-based assays. Five inhibited the enzyme activity of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro by more than 60% at a concentration of 20 μM, and four of them with high potency (IC50 < 10 μM). These hit compounds were further evaluated for their antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in Calu-3 cells. The results from the cell-based assay revealed three mulberry Diels-Alder-type adducts (MDAAs) from Morus alba with pronounced anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities. Sanggenons C (12), O (13), and G (15) showed IC50 values of 4.6, 8.0, and 7.6 μM and selectivity index values of 5.1, 3.1 and 6.5, respectively. The docking poses of MDAAs in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro proposed a butterfly-shaped binding conformation, which was supported by the results of saturation transfer difference NMR experiments and competitive 1H relaxation dispersion NMR spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
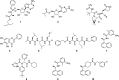

References
-
- World Health Organisation . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed August 18, 2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Miscellaneous

