The rationale, design and baseline data of FLOW, a kidney outcomes trial with once-weekly semaglutide in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 36651820
- PMCID: PMC10469096
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfad009
The rationale, design and baseline data of FLOW, a kidney outcomes trial with once-weekly semaglutide in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The rationale, design and baseline data of FLOW, a kidney outcomes trial with once-weekly semaglutide in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Mar 27;39(4):724. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad252. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38033315 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a common complication of type 2 diabetes (T2D). Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) improve glycaemic control and lower body weight in people with T2D, and some reduce the risk of cardiovascular (CV) events in those with high CV risk. GLP-1RAs might also have kidney-protective effects. We report the design and baseline data for FLOW (NCT03819153), a trial investigating the effects of semaglutide, a once-weekly (OW) GLP-1RA, on kidney outcomes in participants with CKD and T2D.
Methods: FLOW is a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, multinational, phase 3b trial. Participants with T2D, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥50‒≤75 ml/min/1.73 m2 and urine albumin:creatinine ratio (UACR) >300‒<5000 mg/g or eGFR ≥25‒<50 ml/min/1.73 m2 and UACR >100‒<5000 mg/g were randomised 1:1 to OW semaglutide 1.0 mg or matched placebo, with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade (unless not tolerated/contraindicated). The composite primary endpoint is time to first kidney failure (persistent eGFR <15 ml/min/1.73 m2 or initiation of chronic kidney replacement therapy), persistent ≥50% reduction in eGFR or death from kidney or CV causes.
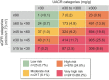
Results: Enrolled participants (N = 3534) had a baseline mean age of 66.6 years [standard deviation (SD) 9.0], haemoglobin A1c of 7.8% (SD 1.3), diabetes duration of 17.4 years (SD 9.3), eGFR of 47.0 ml/min/1.73 m2 (SD 15.2) and median UACR of 568 mg/g (range 2‒11 852). According to Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes guidelines categorisation, 68.2% were at very high risk for CKD progression.
Conclusion: FLOW will evaluate the effect of semaglutide on kidney outcomes in participants with CKD and T2D, and is expected to be completed in late 2024.
Keywords: albuminuria; cardiovascular disease; diabetic kidney disease; glomerular filtration rate; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
P.R. has received grants from Bayer, AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk; received honoraria to the Steno Diabetes Centre Copenhagen from AstraZeneca, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Mundipharma, Sanofi and Bayer; and consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Astellas, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Mundipharma, Sanofi and Bayer. M.G., F.M.M.B., H.B.-T., H.M., J.L., S.G. and T.I. are employees of Novo Nordisk A/S. F.M.M.B., H.B.-T., H.M., S.G. and T.I. also hold stock in Novo Nordisk A/S. G.B. reports consulting fees from Bayer, KBP Biosciences, Ionis, Alnylam, AstraZeneca, Quantum Genomics, Novo Nordisk and Dia Medica Therapeutics. K.W.M. has received consulting fees from Amgen, Applied Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, CSL Behring, Elsevier Fibrogen, Inova, Johnson & Johnson, Lexicon Myokardia, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Otsuka Phasebio, Portola Sanofi and Theravance. J.M. reports grants from Novo Nordisk, the European Union and McMaster University Hamilton, Canada; consulting fees from Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Bayer and Boehringer Ingelheim; honoraria from Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Fresenius and Novartis; and has participated on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for AstraZeneca, Bayer, Sanofi and Boehringer Ingelheim as well as a leadership role in the KDIGO group. V.P. has received honoraria for steering committee, data monitoring committee or advisory board roles or for scientific presentations from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chinook, Dimerix, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Medimmune, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Otsuka, Travere, Tricida and Vifor Pharma; is a Board Director for George Clinical, St. Vincents Health Australia and several independent medical research institutes. K.T. reports grants/contracts from National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)/National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/NIH, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences/NIH, Centers for Disease Control and Travere; consulting fees from Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio, Bayer, Novo Nordisk and AstraZeneca; honoraria from Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Gilead, Goldfinch Bio and Bayer; support for travel and meetings from Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk; has participated on a data safety monitoring board/advisory board for NIDDK/NIH and George Clinical Institute; was Chair of the Diabetic Kidney Disease Collaborative Task Force, American Society of Nephrology and was on the Board of Directors for Kidney Health Initiative, US Food and Drug Administration and the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . Diabetes Atlas, 10th edn.https://diabetesatlas.org/en/resources (15 August 2022, date last accessed).
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Diabetes Work Group . KDIGO 2022 clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2020;102(5 Suppl):S1–127. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association . Standards of medical care in diabetes–2022. Diabetes Care 2022;45(Suppl 1):S1–264. - PubMed
-
- McDermid E. ADA/KDIGO consensus: ‘Speaking the same language’ on CKD management. https://diabetes.medicinematters.com/en-GB/ada-2022/guidelines/ada-kdigo... (18 February 2023, date last accessed).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

