An Adjusted Treatment Comparison Comparing Amivantamab Versus Real-World Clinical Practice in Europe and the United States for Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Activating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
- PMID: 36652175
- PMCID: PMC9988783
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-022-02408-7
An Adjusted Treatment Comparison Comparing Amivantamab Versus Real-World Clinical Practice in Europe and the United States for Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Activating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
Abstract
Introduction: Patients with advanced, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with Exon 20 insertion mutations (Exon20ins) have poor prognoses, exacerbated by a previous lack of specific treatment guidelines and unmet need for targeted therapies. Amivantamab, an EGFR and MET bispecific antibody, demonstrated efficacy and tolerability in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC with Exon20ins following platinum-based therapy in CHRYSALIS (NCT02609776; Cohort D+). Since CHRYSALIS was single-arm, individual patient data (IPD)-based adjusted analyses versus similar patients in real-world clinical practice (RWCP) were conducted to generate comparative evidence.
Methods: RWCP cohorts were derived from seven European and US real-world sources, comprising patients fulfilling CHRYSALIS Cohort D+ eligibility criteria. Amivantamab was compared with a basket of RWCP treatments. Differences in prognostic characteristics were adjusted for using inverse probability weighting (IPW; average treatment effect among the treated [ATT]). Balance between cohorts was assessed using standardized mean differences (SMDs). Overall response rate (ORR; investigator- [INV] and independent review committee-assessed [IRC]), overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS; INV and IRC) and time-to-next treatment (TTNT) were compared. Binary and time-to-event endpoints were analyzed using weighted logistic regression and proportional hazards regression, respectively.
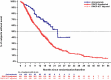
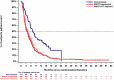
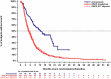
Results: Pre-adjustment, baseline characteristics were comparable between cohorts. IPW ATT-adjustment improved comparability, giving closely matched characteristics. ORR (INV) was 36.8% for amivantamab versus 17.0% for the adjusted EU + US cohort (response rate ratio [RR]: 2.16). Median OS, PFS (INV) and TTNT were 22.77 versus 12.52 months (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.47; p < 0.0001), 6.93 versus 4.17 months (HR: 0.55; p < 0.0001) and 12.42 versus 5.36 months (HR: 0.44; p < 0.0001) for amivantamab versus the adjusted EU + US cohort, respectively. Results were consistent versus EU- and US-only cohorts, and when using IRC assessment.
Conclusion: Adjusted comparisons demonstrated significantly improved outcomes for amivantamab versus RWCP, highlighting the value of amivantamab in addressing unmet need in patients with advanced EGFR Exon20ins NSCLC following platinum-based therapy.
Trial registration: CHRYSALIS: NCT02609776.
Keywords: Adjusted comparison; Amivantamab; Exon 20 insertion mutations; Non-small cell lung cancer; Real-world clinical practice.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
The development of amivantamab for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Respir Res. 2023 Oct 25;24(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02558-4. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37880647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amivantamab versus standard therapies among patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertion mutations after platinum-based therapy in China.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Aug 1;25(1):364. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03826-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40751250 Free PMC article.
-
Amivantamab compared with real-world therapies in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer EGFR Exon 20 insertion mutations after platinum-based chemotherapy.Acta Oncol. 2023 Dec;62(12):1689-1697. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2023.2254479. Epub 2023 Nov 25. Acta Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37938161
-
Amivantamab compared with real-world therapies in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations who progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy.Lung Cancer. 2022 Jun;168:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.03.005. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Lung Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35597172
-
Non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of patient outcomes.Curr Med Res Opin. 2022 Aug;38(8):1341-1350. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2022.2083326. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Curr Med Res Opin. 2022. PMID: 35621011
Cited by
-
Amivantamab Compared with Real-World Physician's Choice after Platinum-Based Therapy from a Pan-European Chart Review of Patients with Lung Cancer and Activating EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 8;15(22):5326. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225326. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001589 Free PMC article.
-
The development of amivantamab for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.Respir Res. 2023 Oct 25;24(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02558-4. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37880647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current clinical practice and physicians' insights on Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer habouring epidermal growth factor receptor 20 insertion mutation.BMC Cancer. 2024 Aug 23;24(1):1043. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12797-3. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39179992 Free PMC article.
-
Amivantamab versus standard therapies among patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertion mutations after platinum-based therapy in China.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Aug 1;25(1):364. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03826-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40751250 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

