AAV Vector Mediated Delivery of NG2 Function Neutralizing Antibody and Neurotrophin NT-3 Improves Synaptic Transmission, Locomotion, and Urinary Tract Function after Spinal Cord Contusion Injury in Adult Rats
- PMID: 36653191
- PMCID: PMC10008066
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1276-22.2023
AAV Vector Mediated Delivery of NG2 Function Neutralizing Antibody and Neurotrophin NT-3 Improves Synaptic Transmission, Locomotion, and Urinary Tract Function after Spinal Cord Contusion Injury in Adult Rats
Abstract
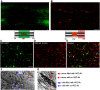
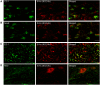
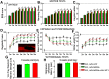
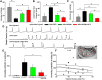
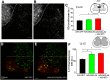
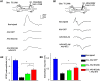
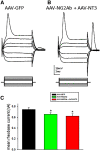
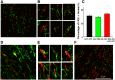
NG2 is a structurally unique transmembrane chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG). Its role in damaged spinal cord is dual. NG2 is considered one of key inhibitory factors restricting axonal growth following spinal injury. Additionally, we have recently detected its novel function as a blocker of axonal conduction. Some studies, however, indicate the importance of NG2 presence in the formation of synaptic contacts. We hypothesized that the optimal treatment would be neutralization of inhibitory functions of NG2 without its physical removal. Acute intraspinal injections of anti-NG2 monoclonal antibodies reportedly prevented an acute block of axonal conduction by exogenous NG2. For prolonged delivery of NG2 function neutralizing antibody, we have developed a novel gene therapy: adeno-associated vector (AAV) construct expressing recombinant single-chain variable fragment anti-NG2 antibody (AAV-NG2Ab). We examined effects of AAV-NG2Ab alone or in combination with neurotrophin NT-3 in adult female rats with thoracic T10 contusion injuries. A battery of behavioral tests was used to evaluate locomotor function. In vivo single-cell electrophysiology was used to evaluate synaptic transmission. Lower urinary tract function was assessed during the survival period using metabolic chambers. Terminal cystometry, with acquisition of external urethral sphincter activity and bladder pressure, was used to evaluate bladder function. Both the AAV-NG2Ab and AAV-NG2Ab combined with AAV-NT3 treatment groups demonstrated significant improvements in transmission, locomotion, and bladder function compared with the control (AAV-GFP) group. These functional improvements associated with improved remyelination and plasticity of 5-HT fibers. The best results were observed in the group that received combinational AAV-NG2Ab+AAV-NT3 treatment.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT We recently demonstrated beneficial, but transient, effects of neutralization of the NG2 proteoglycan using monoclonal antibodies delivered intrathecally via osmotic mini-pumps after spinal cord injury. Currently, we have developed a novel gene therapy tool for prolonged and clinically relevant delivery of a recombinant single-chain variable fragment anti-NG2 antibody: AAV-rh10 serotype expressing scFv-NG2 (AAV-NG2Ab). Here, we examined effects of AAV-NG2Ab combined with transgene delivery of Neurotrophin-3 (AAV-NT3) in adult rats with thoracic contusion injuries. The AAV-NG2Ab and AAV-NG2Ab+AAV-NT3 treatment groups demonstrated significant improvements of locomotor function and lower urinary tract function. Beneficial effects of this novel gene therapy on locomotion and bladder function associated with improved transmission to motoneurons and plasticity of axons in damaged spinal cord.
Keywords: Bladder Function; Locomotion; NG2; Proteoglycan; SCI; Transmission.
Copyright © 2023 the authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of chondroitinase ABC and AAV-NT3 promotes neural plasticity at descending spinal pathways after thoracic contusion in rats.J Neurophysiol. 2013 Oct;110(8):1782-92. doi: 10.1152/jn.00427.2013. Epub 2013 Jul 17. J Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23864374
-
Neutralization of inhibitory molecule NG2 improves synaptic transmission, retrograde transport, and locomotor function after spinal cord injury in adult rats.J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 27;33(9):4032-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4702-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23447612 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed viral vector mediated delivery of neurotrophin-3 improves skilled hindlimb function and stability after thoracic contusion.Exp Neurol. 2023 Feb;360:114278. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2022.114278. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Exp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36455639 Free PMC article.
-
Role of neurotrophins in spinal plasticity and locomotion.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(24):4509-16. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990378. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23360280 Review.
-
Transplants and neurotrophic factors increase regeneration and recovery of function after spinal cord injury.Prog Brain Res. 2002;137:257-73. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(02)37020-1. Prog Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12440372 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro assessment of protamine toxicity with neural cells, its therapeutic potential to counter chondroitin sulfate mediated neuron inhibition, and its effects on reactive astrocytes.Adv Ther (Weinh). 2024 Feb;7(2):2300242. doi: 10.1002/adtp.202300242. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Adv Ther (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39071184 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cytokine networks in neuroinflammatory diseases.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Nov;23(11):862-879. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01026-y. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39261632 Review.
-
Assessing Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction after Spinal Cord Injury: Animal Models in Preclinical Neuro-Urology Research.Biomedicines. 2023 May 26;11(6):1539. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11061539. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37371634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recovery of Forearm and Fine Digit Function After Chronic Spinal Cord Injury by Simultaneous Blockade of Inhibitory Matrix Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan Production and the Receptor PTPσ.J Neurotrauma. 2023 Dec;40(23-24):2500-2521. doi: 10.1089/neu.2023.0117. Epub 2023 Oct 11. J Neurotrauma. 2023. PMID: 37606910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvanian VL, Schnell L, Lou L, Golshani R, Hunanyan A, Ghosh A, Pearse DD, Robinson JK, Schwab ME, Fawcett JW, Mendell LM (2009) Chronic spinal hemisection in rats induces a progressive decline in transmission in uninjured fibers to motoneurons. Exp Neurol 216:471–480. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.01.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arvanian V (2013) Role of neurotrophins in spinal plasticity and locomotion. Curr Pharm Des 19:4509–4516. - PubMed
-
- Arvanian VL, Petrosyan HA, Alessi A, Phagu N, Levine J, Collins WF (2016) Viral vector mediated neutralization of NG2 proteoglycan (AAV-NG2Ab) combined with delivery of neurotrophin NT-3 (AAV-NT3) improves transmission, locomotion and urinary tract function after incomplete spinal cord injury in adult rats. Soc Neurosci Abstract 612:
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
