Blockchain-enabled K-harmonic framework for industrial IoT-based systems
- PMID: 36653424
- PMCID: PMC9849217
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-27739-5
Blockchain-enabled K-harmonic framework for industrial IoT-based systems
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Blockchain-enabled K-harmonic framework for industrial IoT-based systems.Sci Rep. 2024 May 7;14(1):10439. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60626-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38714874 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
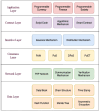
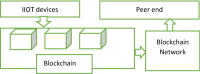
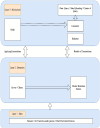
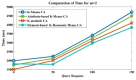
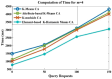
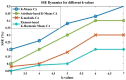
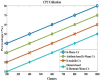
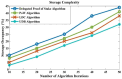
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)-based systems have become an important part of industry consortium systems because of their rapid growth and wide-ranging application. Various physical objects that are interconnected in the IIoT network communicate with each other and simplify the process of decision-making by observing and analyzing the surrounding environment. While making such intelligent decisions, devices need to transfer and communicate data with each other. However, as devices involved in IIoT networks grow and the methods of connections diversify, the traditional security frameworks face many shortcomings, including vulnerabilities to attack, lags in data, sharing data, and lack of proper authentication. Blockchain technology has the potential to empower safe data distribution of big data generated by the IIoT. Prevailing data-sharing methods in blockchain only concentrate on the data interchanging among parties, not on the efficiency in sharing, and storing. Hence an element-based K-harmonic means clustering algorithm (CA) is proposed for the effective sharing of data among the entities along with an algorithm named underweight data block (UDB) for overcoming the obstacle of storage space. The performance metrics considered for the evaluation of the proposed framework are the sum of squared error (SSE), time complexity with respect to different m values, and storage complexity with CPU utilization. The results have experimented with MATLAB 2018a simulation environment. The proposed model has better sharing, and storing based on blockchain technology, which is appropriate IIoT.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Rathee G, Sharma A, Kumar R, Iqbal R. A secure communicating things network framework for industrial IoT using blockchain technology. Ad Hoc Netw. 2019;94:101933. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2019.101933. - DOI
-
- Zhang W, Wu Z, Han G, Feng Y, Shu L. Ldc: A lightweight dada consensus algorithm based on the blockchain for the industrial internet of things for smart city applications. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020;108:574–582. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2020.03.009. - DOI
-
- Ritzdorf H, Soriente C, Karame GO, Marinovic S, Gruber D, Capkun S. Toward shared ownership in the cloud. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018;13(12):3019–3034. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2837648. - DOI
-
- Wang Y. Industrial structure technology upgrade based on 5G network service and IoT intelligent manufacturing. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021;81:103696. doi: 10.1016/j.micpro.2020.103696. - DOI
-
- Kang J, Xiong Z, Niyato D, Ye D, Kim DI, Zhao J. Toward secure blockchain-enabled internet of vehicles: Optimizing consensus management using reputation and contract theory. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019;68(3):2906–2920. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2894944. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

