Magnetically mediated hole pairing in fermionic ladders of ultracold atoms
- PMID: 36653561
- PMCID: PMC9849138
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05437-y
Magnetically mediated hole pairing in fermionic ladders of ultracold atoms
Abstract
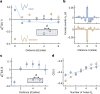
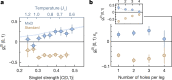
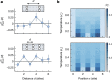
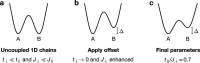
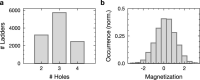
Conventional superconductivity emerges from pairing of charge carriers-electrons or holes-mediated by phonons1. In many unconventional superconductors, the pairing mechanism is conjectured to be mediated by magnetic correlations2, as captured by models of mobile charges in doped antiferromagnets3. However, a precise understanding of the underlying mechanism in real materials is still lacking and has been driving experimental and theoretical research for the past 40 years. Early theoretical studies predicted magnetic-mediated pairing of dopants in ladder systems4-8, in which idealized theoretical toy models explained how pairing can emerge despite repulsive interactions9. Here we experimentally observe this long-standing theoretical prediction, reporting hole pairing due to magnetic correlations in a quantum gas of ultracold atoms. By engineering doped antiferromagnetic ladders with mixed-dimensional couplings10, we suppress Pauli blocking of holes at short length scales. This results in a marked increase in binding energy and decrease in pair size, enabling us to observe pairs of holes predominantly occupying the same rung of the ladder. We find a hole-hole binding energy of the order of the superexchange energy and, upon increased doping, we observe spatial structures in the pair distribution, indicating repulsion between bound hole pairs. By engineering a configuration in which binding is strongly enhanced, we delineate a strategy to increase the critical temperature for superconductivity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bardeen J, Cooper LN, Schrieffer JR. Microscopic theory of superconductivity. Phys. Rev. 1957;106:162–164. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.106.162. - DOI
-
- Scalapino DJ. Superconductivity and spin fluctuations. J. Low Temp. Phys. 1999;117:179–188. doi: 10.1023/A:1022559920049. - DOI
-
- Lee PA, Nagaosa N, Wen X-G. Doping a Mott insulator: physics of high-temperature superconductivity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2006;78:17–85. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.78.17. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

