Platypnea-Orthodeoxia Syndrome: A Rare Cause of Positional Respiratory Failure
- PMID: 36654653
- PMCID: PMC9839979
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32538
Platypnea-Orthodeoxia Syndrome: A Rare Cause of Positional Respiratory Failure
Abstract
Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome (POS) is a rare clinical entity characterized by dyspnea and arterial desaturation in the upright position. Hypoxia in POS has been attributed to the mixing of deoxygenated venous with oxygenated arterial blood via a shunt, with patent foramen ovale being the most commonly reported abnormality. A systematic evaluation is necessary to identify the underlying cause and promote an appropriate intervention. Here, we present the case of a 79-year-old female with a new diagnosis of POS during the workup of hypoxemic respiratory failure.
Keywords: atrial septal defects occluder; hypoxemic respiratory failure; patent foramen ovale; platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome; positional dyspnea.
Copyright © 2022, Soares et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
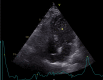
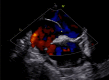
References
-
- The multiple dimensions of platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome: a review. Agrawal A, Palkar A, Talwar A. Respir Med. 2017;129:31–38. - PubMed
-
- Reflex orthostatic dyspnea associated with pulmonary hypotension. Burchell HB, Wood EH. https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1572824499151551104 Am J Physiol. 1949;159:563–564.
-
- Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome in review: defining a new disease? Rodrigues P, Palma P, Sousa-Pereira L. Cardiology. 2012;123:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome after complicated cholecystectomy: an unsuspected diagnosis. Queirós C, Francisco E, Almeida J. Acta Med Port. 2017;30:827–830. - PubMed
-
- The platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome. Akin E, Krüger U, Braun P, et al. http://www.europeanreview.org/wp/wp-content/uploads/2599-26041.pdf. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18:2599–2604. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
