Activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression by thymic B cells promotes T-cell tolerance and limits autoimmunity
- PMID: 36654860
- PMCID: PMC9840937
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105852
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase expression by thymic B cells promotes T-cell tolerance and limits autoimmunity
Abstract
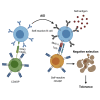
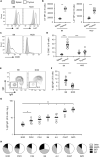
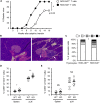
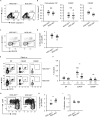
Elimination of self-reactive T cells in the thymus is critical to establish T-cell tolerance. A growing body of evidence suggests a role for thymic B cells in the elimination of self-reactive thymocytes. To specifically address the role of thymic B cells in central tolerance, we investigated the phenotype of thymic B cells in various mouse strains, including non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, a model of autoimmune diabetes. We noted that isotype switching of NOD thymic B cells is reduced as compared to other, autoimmune-resistant, mouse strains. To determine the impact of B cell isotype switching on thymocyte selection and tolerance, we generated NOD.AID-/- mice. Diabetes incidence was enhanced in these mice. Moreover, we observed reduced clonal deletion and a resulting increase in self-reactive CD4+ T cells in NOD.AID-/- mice relative to NOD controls. Together, this study reveals that AID expression in thymic B cells contributes to T-cell tolerance.
Keywords: Immunity; Immunology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase deficiency accelerates autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice.JCI Insight. 2018 Jan 11;3(1):e95882. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.95882. eCollection 2018 Jan 11. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 29321370 Free PMC article.
-
Defective thymic T cell activation by concanavalin A and anti-CD3 in autoimmune nonobese diabetic mice. Evidence for thymic T cell anergy that correlates with the onset of insulitis.J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3763-71. J Immunol. 1991. PMID: 1827815
-
MHC-mismatched mixed chimerism mediates thymic deletion of cross-reactive autoreactive T cells and prevents insulitis in nonobese diabetic mice.J Immunol. 2015 Jan 1;194(1):407-17. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401584. Epub 2014 Nov 26. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25429069
-
Thymic commitment of regulatory T cells is a pathway of TCR-dependent selection that isolates repertoires undergoing positive or negative selection.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;293:43-71. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27702-1_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15981475 Review.
-
Transgenic models of T-cell self tolerance and autoimmunity.Immunol Rev. 1990 Dec;118:21-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00812.x. Immunol Rev. 1990. PMID: 2079327 Review.
Cited by
-
Thymus antibody-secreting cells: once forgotten but not lost.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 12;14:1170438. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1170438. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37122712 Free PMC article.
-
Thymflammation: The Role of a Constitutively Active Inflammatory Network and "Ectopic" Cell Types in the Thymus in the Induction of T Cell Tolerance and Beyond.Immunol Rev. 2025 Jul;332(1):e70037. doi: 10.1111/imr.70037. Immunol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40433806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antigen presentation for central tolerance induction.Nat Rev Immunol. 2025 Jan;25(1):57-72. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01076-8. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39294277 Review.
-
Thymic B cells in aging and autoimmune disease.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 23;16:1595805. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1595805. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40625741 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

