Erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia following percutaneous nephrolithotomy under spinal anaesthesia- A randomised controlled study
- PMID: 36654902
- PMCID: PMC9842086
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.ija_692_21
Erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia following percutaneous nephrolithotomy under spinal anaesthesia- A randomised controlled study
Abstract
Background and aims: Postoperative pain is a multitude of various irksome sensory, emotional and mental experiences aggravated by surgical trauma and associated with autonomic, endocrine, metabolic, physiological and behavioural responses. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of erector spinae plane block (ESPB) in postoperative analgesia following percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) under spinal anaesthesia.
Methods: This prospective randomised study was conducted on sixty American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I and II patients scheduled for PCNL under spinal anaesthesia. They were randomised into two equal groups of thirty patients. ESPB was given in group A with 20 ml of injection bupivacaine 0.25% and dexamethasone 8 mg and group B received injection tramadol 1.5 mg/kg intravenously immediately after PCNL. The primary outcome was comparison of visual analogue scale (VAS) score in the first 24 h postoperatively, whereas secondary objectives included hemodynamic variables and requirement of rescue analgesia.
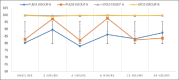
Results: VAS score in group A (ESPB) with mean of 3.15 ± 0.68 was comparatively low when compared to group B with mean of 6.61 ± 0.50 at 6 hours. After 4 h postoperatively, VAS scores continued to be higher and significant number of patients required rescue analgesia in group B.
Conclusion: ESPB reduced VAS score, provided adequate postoperative analgesia, with similar haemodynamic changes and adverse effects in comparison to the conventional analgesia with tramadol in PCNL.
Keywords: Nephrolithotomy; pain; percutaneous; regional anaesthesia; tramadol.
Copyright: © 2022 Indian Journal of Anaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ford DJ, Raj PP, Singh P, Regan KM, Ohlweiler D. Differential peripheral nerve block by local anesthetics in the cat. Anesthesiology. 1984;60:28–33. - PubMed
-
- Chin KJ, Adhikary SD, Forero M. Understanding ESP and fascial plane blocks:A challenge to omniscience. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018;43:807–8. - PubMed
-
- Kunigo T, Murouchi T, Yamamoto S, Yamakage M. Injection volume and anesthetic effect in serratus plane block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2017;42:737–40. - PubMed
-
- Kumar GS, Balakundi P, Deo A. ESRA19-0663A new indication of erector spinae plane block for perioperative analgesia is percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) surgery:case series. Regional Anesthesia &Pain Medicine. 2019;44:A254–A255.
-
- Bakshi A, Srivastawa S, Jadon A, Mohsin K, Sinha N, Chakraborty S. Comparison of the analgesic efficacy of ultrasound-guided transmuscular quadratus lumborum block versus thoracic erector spinae block for postoperative analgesia in caesarean section parturients under spinal anaesthesia—A randomised study. Indian J Anaesth. 2022;66:S213–9. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources