Inulin-type fructans and short-chain fructooligosaccharides-their role within the food industry as fat and sugar replacers and texture modifiers-what needs to be considered!
- PMID: 36655109
- PMCID: PMC9834882
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3040
Inulin-type fructans and short-chain fructooligosaccharides-their role within the food industry as fat and sugar replacers and texture modifiers-what needs to be considered!
Abstract
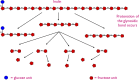
Inulin and oligofructose are classes of prebiotics belonging to a group of nondigestible carbohydrates referred to as inulin-type fructans. While short-chain fructooligosaccharides are enzymatically synthesized from the hydrolysis and transglycosylation of sucrose. Inulin-type fructans and short-chain fructooligosaccharides act as carbon sources for selective pathways supporting digestive health including altering the composition of the gut microbiota along with improving transit time. Due to their physicochemical properties, inulin-type fructans and short-chain fructooligosaccharides have been widely used in the food industry as partial replacements for both fat and sugar. Yet, levels of replacement need to be carefully considered as it may result in changes to physical and sensory properties that could be detected by consumers. Furthermore, it has been reported depending on the processing parameters used during production that inulin-type fructans and short-chain fructooligosaccharides may or may not undergo structural alterations. Therefore, this paper reviews the role of inulin-type fructans and short-chain fructooligosaccharides within the food industry as fat and sugar replacers and texture modifiers, their impact on final sensory properties, and to what degree processing parameters are likely to impact their functional properties.
Keywords: carbohydrates; chemistry; food processing; inulin; physical; polysaccharides; prebiotics; sensory.
© 2022 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Afshari, R. , Hosseini, H. , Khaksar, R. , Mohammadifar, M. A. , Amiri, Z. , Komeili, R. , & Khaneghah, A. M. (2015). Investigation of the effects of inulin and β‐glucan on the physical and sensory properties of low‐fat beef burgers containing vegetable oils: Optimisation of the formulation using D‐optimal mixture design. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 53(4), 436–445. 10.17113/ftb.53.04.15.3980 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aidoo, R. P. , Afoakwa, E. O. , & Dewettinck, K. (2014). Optimization of inulin and polydextrose mixtures as sucrose replacers during sugar‐free chocolate manufacture ‐ rheological, microstructure and physical quality characteristics. Journal of Food Engineering, 126, 35–42. 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.10.036 - DOI
-
- Aidoo, R. P. , Depypere, F. , Afoakwa, E. O. , & Dewettinck, K. (2013). Industrial manufacture of sugar‐free chocolates ‐ applicability of alternative sweeteners and carbohydrate polymers as raw materials in product development. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 32(2), 84–96. 10.1016/j.tifs.2013.05.008 - DOI
-
- Akbari, M. , Eskandari, M. H. , & Davoudi, Z. (2019). Application and functions of fat replacers in low‐fat ice cream: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 86, 34–40. 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.02.036 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

