Metabolism of sumatriptan revisited
- PMID: 36655303
- PMCID: PMC9849828
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.1051
Metabolism of sumatriptan revisited
Abstract
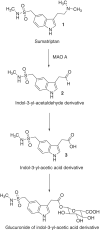
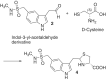
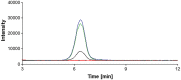
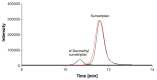
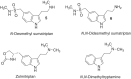
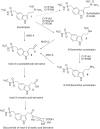
Scientific literature describes that sumatriptan is metabolized by oxidative deamination of its dimethylaminoethyl residue by monoamine oxidase A (MAO A) and not by cytochrome P450 (CYP)-mediated demethylation, as is usual for such structural elements. Using recombinant human enzymes and HPLC-MS analysis, we found that CYP enzymes may also be involved in the metabolism of sumatriptan. The CYP1A2, CYP2C19, and CYP2D6 isoforms converted this drug into N-desmethyl sumatriptan, which was further demethylated to N,N-didesmethyl sumatriptan by CYP1A2 and CYP2D6. Otherwise, sumatriptan and its two desmethyl metabolites were metabolized by recombinant MAO A but not by MAO B to the corresponding acetaldehyde, with sumatriptan being only a poor substrate for MAO A compared to the N-demethylated and the N,N-didemethylated derivatives.
Keywords: cytochrome P450; metabolism; monoamine oxidase; sumatriptan; zolmitriptan.
© 2023 The Authors. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Karki SB, Dinnocenzo JP. On the mechanism of amine oxidations by P450. Xenobiotica. 1995;25:711‐724. - PubMed
-
- Benedetti MS. Biotransformation of xenobiotics by amine oxidases. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2001;15:75‐84. - PubMed
-
- Tipton KF, Benedetti MS. Amine oxidases and the metabolism of xenobiotics. In: Ioannidis C, ed. Enzyme Systems that Metabolize Drugs and Other Xenobiotics. Wiley & Sons Ltd; 2001.
-
- Lang D, Kalgutkar AS. Non‐P450 mediated oxidative metabolism of xenobiotics. In: Lee JS, Obach RS, Fisher MB, eds. Drug Metabolizing Enzymes. Marcel Dekker; 2003:483‐539.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

