Immunological and inflammatory effects of infectious diseases in circadian rhythm disruption and future therapeutic directions
- PMID: 36656437
- PMCID: PMC9851103
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-023-08276-w
Immunological and inflammatory effects of infectious diseases in circadian rhythm disruption and future therapeutic directions
Abstract
Background: Circadian rhythm is characterised by daily variations in biological activity to align with the light and dark cycle. These diurnal variations, in turn, influence physiological functions such as blood pressure, temperature, and sleep-wake cycle. Though it is well established that the circadian pathway is linked to pro-inflammatory responses and circulating immune cells, its association with infectious diseases is widely unknown.
Objective: This comprehensive review aims to describe the association between circadian rhythm and host immune response to various kinds of infection.
Methods: We conducted a literature search in databases Pubmed/Medline and Science direct. Our paper includes a comprehensive analysis of findings from articles in English which was related to our hypothesis.
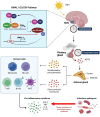
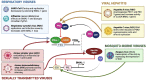
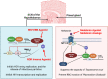
Findings: Molecular clocks determine circadian rhythm disruption in response to infection, influencing the host's response toward infection. Moreover, there is a complex interplay with intrinsic oscillators of pathogens and the influence of specific infectious processes on the CLOCK: BMAL1 pathway. Such mechanisms vary for bacterial and viral infections, both well studied in the literature. However, less is known about the association of parasitic infections and fungal pathogens with circadian rhythm modulation.
Conclusion: It is shown that bidirectional relationships exist between circadian rhythm disruption and infectious process, which contains interplay between the host's and pathogens' circadian oscillator, immune response, and the influence of specific infectious. Further studies exploring the modulations of circadian rhythm and immunity can offer novel explanations of different susceptibilities to infection and can lead to therapeutic avenues in circadian immune modulation of infectious diseases.
Keywords: Chrono-immunology; Circadian rhythm; Immune response; Infectious diseases; Inflammation; Melatonin; Molecular clocks.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Macrophage Meets the Circadian Clock: Implication of the Circadian Clock in the Role of Macrophages in Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 23;12:826738. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.826738. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35281442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chrono-immunology: progress and challenges in understanding links between the circadian and immune systems.Immunology. 2015 Nov;146(3):349-58. doi: 10.1111/imm.12525. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 26301993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil infiltration regulates clock-gene expression to organize daily hepatic metabolism.Elife. 2020 Dec 8;9:e59258. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59258. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33287957 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Circadian Rhythms and Sleep in Critical Illness and its Impact on Innate Immunity.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(24):3469-76. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150706105034. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26144943 Review.
-
The Relationship between Circadian Rhythm and Cancer Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 28;25(11):5846. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115846. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892035 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian syndrome and mortality risk in adults aged ≥ 40 years: a prospective cohort analysis of CHARLS and NHANES.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 28;15(1):14791. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99631-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40295832 Free PMC article.
-
BMAL2 promotes eCIRP-induced macrophage endotoxin tolerance.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 13;15:1426682. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1426682. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38938563 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the biorhythm in gastric epithelial cell triggers inflammation in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis by aberrantly regulating NFIL3 via CagA activated ERK-SP1 pathway.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jun 15;23(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02302-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40518541 Free PMC article.
-
The Complex Relationship Between Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease With Cardiovascular Disease and Their Interactions With COVID-19 Vaccination: A Retrospective Study.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Nov;12(11):e70068. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70068. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39555721 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the circadian rhythm signaling pathway in HTLV-1 pathogenesis using Boolean analysis.Virus Res. 2025 Mar;353:199539. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2025.199539. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Virus Res. 2025. PMID: 39892646 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

