Promoting Molecular Exchange on Rare-Earth Oxycarbonate Surfaces to Catalyze the Water-Gas Shift Reaction
- PMID: 36657461
- PMCID: PMC9896556
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c10326
Promoting Molecular Exchange on Rare-Earth Oxycarbonate Surfaces to Catalyze the Water-Gas Shift Reaction
Abstract
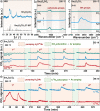
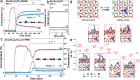
It is highly desirable to fabricate an accessible catalyst surface that can efficiently activate reactants and desorb products to promote the local surface reaction equilibrium in heterogeneous catalysis. Herein, rare-earth oxycarbonates (Ln2O2CO3, where Ln = La and Sm), which have molecular-exchangeable (H2O and CO2) surface structures according to the ordered layered arrangement of Ln2O22+ and CO32- ions, are unearthed. On this basis, a series of Ln2O2CO3-supported Cu catalysts are prepared through the deposition precipitation method, which provides excellent catalytic activity and stability for the water-gas shift (WGS) reaction. Density functional theory calculations combined with systematic experimental characterizations verify that H2O spontaneously dissociates on the surface of Ln2O2CO3 to form hydroxyl by eliminating the carbonate through the release of CO2. This interchange efficiently promotes the WGS reaction equilibrium shift on the local surface and prevents the carbonate accumulation from hindering the active sites. The discovery of the unique layered structure provides a so-called "self-cleaning" active surface for the WGS reaction and opens new perspectives about the application of rare-earth oxycarbonate nanomaterials in C1 chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Tsai C. H.; Chen H. T.; Althaus S. M.; Mao K.; Kobayashi T.; Pruski M.; Lin V. S. Y. Rational Catalyst Design: A Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Catalyst for Shifting the Reaction Equilibrium by Removal of Byproduct. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 729–732. 10.1021/cs200222t. - DOI
-
- Wei L. Y.; Azad H.; Haije W.; Grenman H.; de Jong W. Pure methane from CO2 hydrogenation using a sorption enhanced process with catalyst/zeolite bifunctional materials. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2021, 297, 120399. 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120399. - DOI
-
- Huang W. J.; Yu C. T.; Sheu W. J.; Chen Y. C. The effect of non-uniform temperature on the sorption-enhanced steam methane reforming in a tubular fixed-bed reactor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 2021, 46, 16522–16533. 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.07.182. - DOI
-
- Wang H.; Wang L.; Lin D.; Feng X.; Niu Y. M.; Zhang B. S.; Xiao F. S. Strong metal–support interactions on gold nanoparticle catalysts achieved through Le Chatelier’s principle. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 418–424. 10.1038/s41929-021-00611-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

