Polymer-based drug delivery systems under investigation for enzyme replacement and other therapies of lysosomal storage disorders
- PMID: 36657645
- PMCID: PMC10629597
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114683
Polymer-based drug delivery systems under investigation for enzyme replacement and other therapies of lysosomal storage disorders
Abstract
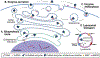
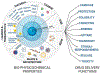
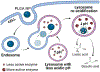
Lysosomes play a central role in cellular homeostasis and alterations in this compartment associate with many diseases. The most studied example is that of lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs), a group of 60 + maladies due to genetic mutations affecting lysosomal components, mostly enzymes. This leads to aberrant intracellular storage of macromolecules, altering normal cell function and causing multiorgan syndromes, often fatal within the first years of life. Several treatment modalities are available for a dozen LSDs, mostly consisting of enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) strategies. Yet, poor biodistribution to main targets such as the central nervous system, musculoskeletal tissue, and others, as well as generation of blocking antibodies and adverse effects hinder effective LSD treatment. Drug delivery systems are being studied to surmount these obstacles, including polymeric constructs and nanoparticles that constitute the focus of this article. We provide an overview of the formulations being tested, the diseases they aim to treat, and the results observed from respective in vitro and in vivo studies. We also discuss the advantages and disadvantages of these strategies, the remaining gaps of knowledge regarding their performance, and important items to consider for their clinical translation. Overall, polymeric nanoconstructs hold considerable promise to advance treatment for LSDs.
Keywords: Cellular and animal models; Enzyme replacement therapy; Lysosomal storage disorders; Nanoemulsions; Nanoparticles; Polymer-based drug delivery systems.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
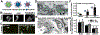
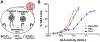
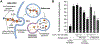
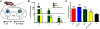
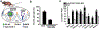
References
-
- Holtzman E, Historical Fragments; Methods; Some Terminology, in: Lysosomes. Cellular Organelles Series Springer; New York, NY, 1989, pp. 1–24. 10.1007/978-1-4899-2540-4.. - DOI
-
- Seaman MNJ, Burd CG, Emr SD, Receptor signalling and the regulation of endocytic membrane transport, Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 8 (1996) 549–556, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0955-0674(96)80034-2. - DOI - PubMed

