Hepatocyte growth factor-mediated apoptosis mechanisms of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells in normal and cirrhotic livers
- PMID: 36658107
- PMCID: PMC9852593
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-023-01313-4
Hepatocyte growth factor-mediated apoptosis mechanisms of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells in normal and cirrhotic livers
Abstract
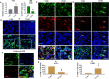
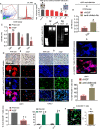
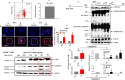
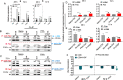
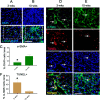
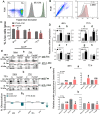
Intrahepatic stem/progenitor cells and cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (CD8+ T cells) in the cirrhotic liver undergo apoptosis, which potentially facilitates progression to cancer. Here, we report that hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) signaling plays an important role in promoting normal and damaged liver CD8+ T cell Fas-mediated apoptosis through its only receptor, c-Met. In addition to binding with HGF, c-Met also binds to Fas to form a complex. Using a diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced liver fibrosis/cirrhosis mouse model, immunostaining, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining, we found that HGF secretion was significantly higher at 10 weeks post-DEN, the liver cirrhotic phase (LCP), than at 3 weeks post-DEN, the liver fibrotic phase (LFP). Correspondingly, differences in CD8+ T cell proliferation and apoptosis were noted between the two phases. Interestingly, staining and TUNEL assays revealed lower smooth muscle actin (α-SMA)+ cell apoptosis, a marker for hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), in the LFP group than in the LCP group, which suggested a beneficial correlation among HGF, CD8+ T cells and HSCs in improving the fibrotic load during damaged liver repair. In cultures, when met different concentrations of recombinant HGF (rHGF), phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-stimulated naive mouse splenic CD8+ T cells (pn-msCD8+ T cells) responded differently; as increases in rHGF increased were associated with decreases in the clonal numbers of pn-msCD8+ T cells, and when the rHGF dose was greater than 200 ng/mL, the clonal numbers significantly decreased. In the presence of 400 ng/mL rHGF, the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) can be directly activated in both nsCD8+ T cells and healthy human peripheral blood CD8+ T cells (hp-CD8+ T cells), as indicated by recruitment of FADD and caspase-8 because DISC forms via the recruitment of FADD and caspase-8, among others. These findings suggest that Fas-mediated apoptosis, may also indicate a regulatory role of HGF signaling in hepatic homeostasis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human platelets inhibit liver fibrosis in severe combined immunodeficiency mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Aug 28;19(32):5250-60. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5250. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23983427 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulating HGF signaling reshapes the cirrhotic liver niche and fills a therapeutic gap in regeneration mediated by transplanted stem cells.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Jan 1;434(1):113867. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113867. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38043723
-
Antifibrotic effect of hepatocyte growth factor-expressing mesenchymal stem cells in small-for-size liver transplant rats.Stem Cells Dev. 2010 Jun;19(6):903-14. doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0254. Stem Cells Dev. 2010. PMID: 20025519
-
Cooperation of liver cells in health and disease.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001;161:III-XIII, 1-151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-56553-3. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11729749 Review.
-
Soluble HLA class I molecules/CD8 ligation trigger apoptosis of CD8+ cells by Fas/Fas-ligand interaction.ScientificWorldJournal. 2002 Feb 12;2:421-3. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2002.122. ScientificWorldJournal. 2002. PMID: 12806026 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro differentiated human CD4+ T cells produce hepatocyte growth factor.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 13;14:1210836. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1210836. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37520551 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Role of HGF/c-Met Signaling in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumor Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 22;25(16):9101. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169101. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative effects of hepatocyte growth factor and tacrolimus on acute liver allograft early tolerance.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 8;14:1162439. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1162439. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37614233 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

