Immune correlates analysis of the PREVENT-19 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial
- PMID: 36658109
- PMCID: PMC9851580
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35768-3
Immune correlates analysis of the PREVENT-19 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Immune correlates analysis of the PREVENT-19 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 22;14(1):1581. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37367-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36949083 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
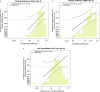
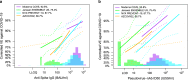
In the PREVENT-19 phase 3 trial of the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine (NCT04611802), anti-spike binding IgG concentration (spike IgG), anti-RBD binding IgG concentration (RBD IgG), and pseudovirus 50% neutralizing antibody titer (nAb ID50) measured two weeks post-dose two are assessed as correlates of risk and as correlates of protection against COVID-19. Analyses are conducted in the U.S. cohort of baseline SARS-CoV-2 negative per-protocol participants using a case-cohort design that measures the markers from all 12 vaccine recipient breakthrough COVID-19 cases starting 7 days post antibody measurement and from 639 vaccine recipient non-cases. All markers are inversely associated with COVID-19 risk and directly associated with vaccine efficacy. In vaccine recipients with nAb ID50 titers of 50, 100, and 7230 international units (IU50)/ml, vaccine efficacy estimates are 75.7% (49.8%, 93.2%), 81.7% (66.3%, 93.2%), and 96.8% (88.3%, 99.3%). The results support potential cross-vaccine platform applications of these markers for guiding decisions about vaccine approval and use.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures




References
-
- Nextstrain Team. Nexstrain. Genomic epidemiology of novel coronavirus—global subsampling. https://nextstrain.org/ncov/gisaid/global. (2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI148689/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028685/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 AI174104/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- C0000008/CL/CLC NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068614/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068618/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI054165/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI148684/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068635/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068619/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068614/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068617/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

