YTHDF2 orchestrates tumor-associated macrophage reprogramming and controls antitumor immunity through CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 36658237
- PMCID: PMC10150872
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-022-01398-6
YTHDF2 orchestrates tumor-associated macrophage reprogramming and controls antitumor immunity through CD8+ T cells
Abstract
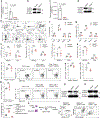
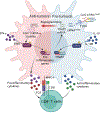
Despite tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) playing a key role in shaping the tumor microenvironment (TME), the mechanisms by which TAMs influence the TME and contribute to cancer progression remain unclear. Here, we show that the N6-methyladenosine reader YTHDF2 regulates the antitumor functions of TAMs. YTHDF2 deficiency in TAMs suppressed tumor growth by reprogramming TAMs toward an antitumoral phenotype and increasing their antigen cross-presentation ability, which in turn enhanced CD8+ T cell-mediated antitumor immunity. YTHDF2 deficiency facilitated the reprogramming of TAMs by targeting interferon-γ-STAT1 signaling. The expression of YTHDF2 in TAMs was regulated by interleukin-10-STAT3 signaling. Selectively targeting YTHDF2 in TAMs using a Toll-like receptor 9 agonist-conjugated small interfering RNA reprogrammed TAMs toward an antitumoral phenotype, restrained tumor growth and enhanced the efficacy of PD-L1 antibody therapy. Collectively, our findings describe the role of YTHDF2 in orchestrating TAMs and suggest that YTHDF2 inhibition is an effective approach to enhance cancer immunotherapy.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


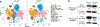
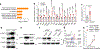

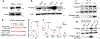







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS106170/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N99020D00005/OF/ORFDO NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA266457/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA210087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA264512/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N95020D00005/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA163205/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA247550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA265095/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N93023D00005/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI129582/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA223400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N93022D00005/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

