Cytosolic aldose metabolism contributes to progression from cirrhosis to hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 36658399
- PMCID: PMC9892301
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-022-00711-9
Cytosolic aldose metabolism contributes to progression from cirrhosis to hepatocarcinogenesis
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Cytosolic aldose metabolism contributes to progression from cirrhosis to hepatocarcinogenesis.Nat Metab. 2023 Feb;5(2):349. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00752-8. Nat Metab. 2023. PMID: 36755183 No abstract available.
Abstract
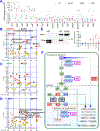
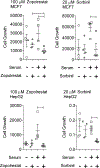
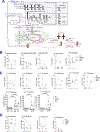
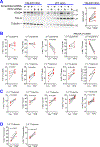
Oxidative stress modulates carcinogenesis in the liver; however, direct evidence for metabolic control of oxidative stress during pathogenesis, particularly, of progression from cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), has been lacking. Deficiency of transaldolase (TAL), a rate-limiting enzyme of the non-oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), restricts growth and predisposes to cirrhosis and HCC in mice and humans. Here, we show that mitochondrial oxidative stress and progression from cirrhosis to HCC and acetaminophen-induced liver necrosis are critically dependent on NADPH depletion and polyol buildup by aldose reductase (AR), while this enzyme protects from carbon trapping in the PPP and growth restriction in TAL deficiency. Both TAL and AR are confined to the cytosol; however, their inactivation distorts mitochondrial redox homeostasis in opposite directions. The results suggest that AR acts as a rheostat of carbon recycling and NADPH output of the PPP with broad implications for disease progression from cirrhosis to HCC.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
The authors declare having no competing interests.
Figures
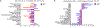

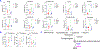







References
-
- Sung H et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin 71, 209–249 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

