Acetyl-CoA metabolism in cancer
- PMID: 36658431
- PMCID: PMC11137663
- DOI: 10.1038/s41568-022-00543-5
Acetyl-CoA metabolism in cancer
Abstract
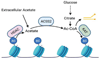
Few metabolites can claim a more central and versatile role in cell metabolism than acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA). Acetyl-CoA is produced during nutrient catabolism to fuel the tricarboxylic acid cycle and is the essential building block for fatty acid and isoprenoid biosynthesis. It also functions as a signalling metabolite as the substrate for lysine acetylation reactions, enabling the modulation of protein functions in response to acetyl-CoA availability. Recent years have seen exciting advances in our understanding of acetyl-CoA metabolism in normal physiology and in cancer, buoyed by new mouse models, in vivo stable-isotope tracing approaches and improved methods for measuring acetyl-CoA, including in specific subcellular compartments. Efforts to target acetyl-CoA metabolic enzymes are also advancing, with one therapeutic agent targeting acetyl-CoA synthesis receiving approval from the US Food and Drug Administration. In this Review, we give an overview of the regulation and cancer relevance of major metabolic pathways in which acetyl-CoA participates. We further discuss recent advances in understanding acetyl-CoA metabolism in normal tissues and tumours and the potential for targeting these pathways therapeutically. We conclude with a commentary on emerging nodes of acetyl-CoA metabolism that may impact cancer biology.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
DAG and KEW have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Sugden MC & Holness MJ Recent advances in mechanisms regulating glucose oxidation at the level of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex by PDKs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284, E855–62 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Adina-Zada A. et al. Allosteric regulation of the biotin-dependent enzyme pyruvate carboxylase by acetyl-CoA. Biochem Soc Trans 40, 567–72 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

