Brain and gut microbiota disorders in the psychopathology of anorexia nervosa
- PMID: 36660007
- PMCID: PMC9824428
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0267
Brain and gut microbiota disorders in the psychopathology of anorexia nervosa
Abstract
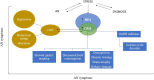
Studies of pathophysiological mechanisms involved in eating disorders (EDs) have intensified over the past several years, revealing their unprecedented and unanticipated complexity. Results from many articles highlight critical aspects in each member of ED family. Notably, anorexia nervosa (AN) is a disorder due to undefined etiology, frequently associated with symptoms of depression, anxiety, obsessive-compulsiveness, accompanied by endocrine alterations, altered immune response, increased inflammation, and dysbiosis of the gut microbiota. Hence, an advanced knowledge of how and why a multisystem involvement exists is of paramount importance to understand the pathogenetic mechanisms of AN. In this review, we describe the change in the brain structure/function focusing on hypothalamic endocrine disorders and the disequilibrium of gut microbiota in AN that might be responsible for the psychopathological complication.
Keywords: anorexia nervosa; eating disorders; gut microbiota; hypothalamic disorders.
© 2022 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Filion AJ, Haines J. Why prevention? The case for upstream strategies. In: Smolak L, Levine MP, editors. The Wiley handbook of eating disorders. Wiley online library; 2015. p. 557–68.
-
- Bakalar JL, Shank LM, Vannucci A, Radin RM, Tanofsky-Kraff M. In: Grilo C, editor. Recent advances in developmental and risk factor research on eating disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015;17:42. - PubMed
-
- Esposito R, Bortoletto M, Miniussi C. Integrating TMS, EEG, and MRI as an approach for studying brain connectivity. Neuroscientist. 2020;26:471–86. - PubMed
-
- Castro-Fornieles J, Bargalló N, Lázaro L, Andrés S, Falcon C, Plana MT, et al. A cross-sectional and follow-up voxel-based morphometric MRI study in adolescent anorexia nervosa. J Psych Res. 2009;43:331–40. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
