What Is the Long-Term Findings of Olfactory and Taste Loss due to COVID-19?
- PMID: 36660391
- PMCID: PMC9833342
- DOI: 10.14744/SEMB.2022.56492
What Is the Long-Term Findings of Olfactory and Taste Loss due to COVID-19?
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study was to determine prevalance, severity, course, and long-term findings of smell and taste disorders of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients in mild-moderate and severe-critical disease spectrum.
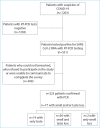
Methods: All adult patients conducted in our hospital with positive severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 between March and April 2020 were surveyed during disease course and those with olfactory and taste loss were re-surveyed to determine the course and progress of these symptoms after at least 12-month follow-up. Demographic features and clinical findings were evaluated as well as disease severity.
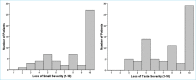
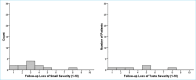
Results: A total of 77 patients with smell and/or taste loss symptoms were included in the study. At diagnosis, 58 (75.3%) patients had loss of smell and 75 (97.4%) had loss of taste. After a follow-up period of 12-14 months, 12 (15.6%) patients had ongoing loss of smell and six (8%) patients had ongoing loss of taste. Three (3.9%) patients complained of cacosmia and 5 (6.5%) complained of parosmia at follow-up. The presence of ongoing visual analog scale scores of smell and/or taste was not statistically significant between male and female patients. When presence and severity of symptoms were compared by disease severity, no statistically significant difference was found.
Conclusion: Smell and taste loss seem to be among the presenting symptoms of COVID-19. The prognosis and the treatment of the smell loss and taste loss in COVID-19 patients remains unclear. To improve and accelerate recovery, the pathophysiology and the treatment options must be validated.
Keywords: COVID-19; olfaction; smell; taste.
©Copyright 2022 by The Medical Bulletin of Sisli Etfal Hospital.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-reported Taste and Smell Disorders in Patients with COVID-19: Distinct Features in China.Curr Med Sci. 2021 Feb;41(1):14-23. doi: 10.1007/s11596-021-2312-7. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Curr Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33582900 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Loss of Smell and/or Taste and other Otorhinolaryngology Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients.Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2021 Apr-Jun;19(74):173-179. Kathmandu Univ Med J (KUMJ). 2021. PMID: 34819431
-
Recovery rate and factors associated with smell and taste disruption in patients with coronavirus disease 2019.Am J Otolaryngol. 2021 Sep-Oct;42(5):102648. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102648. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Am J Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 33799139 Free PMC article.
-
Sudden onset, acute loss of taste and smell in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systematic review.Acta Odontol Scand. 2020 Aug;78(6):467-473. doi: 10.1080/00016357.2020.1787505. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Acta Odontol Scand. 2020. PMID: 32762282
-
Potential pharmacologic treatments for COVID-19 smell and taste loss: A comprehensive review.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 5;912:174582. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174582. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34678243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Living and Coping with Olfactory and Taste Disorders: A Qualitative Study of People with Long-COVID-19.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Mar 30;12(7):754. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12070754. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38610176 Free PMC article.
-
The assessment of qualitative olfactory dysfunction in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review of tools and their content validity.Front Psychol. 2023 Jun 20;14:1190994. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1190994. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37408960 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
