Effect of miR-21-3p on lung injury in rats with traumatic hemorrhagic shock resuscitated with sodium bicarbonate Ringer's solution
- PMID: 36660723
- PMCID: PMC9843335
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-5148
Effect of miR-21-3p on lung injury in rats with traumatic hemorrhagic shock resuscitated with sodium bicarbonate Ringer's solution
Abstract
Background: Restricted fluid resuscitation is the most important early method for treating traumatic hemorrhagic shock (THS). This study sought to explore whether micro ribonucleic acid (miR)-21-3p affected resuscitated THS rats by regulating the glycocalyx and inflammation.
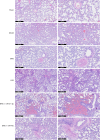
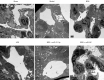
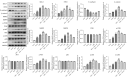
Methods: MiRNAs extracted from the lung tissues were analyzed by miRNA microarray assays. A rat model of THS was induced by hemorrhage from a left femur fracture. The pathological change in the lung tissues and glycocalyx structure was observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining and a transmission electron microscope examination. The miR-21-3p expression in the lung tissues and serum was detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The levels of glycocalyx-related factors and inflammation-related factors were determined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assays. The expression of glycocalyx-related proteins, cell junction-related proteins, and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway-related proteins was analyzed by Western blot.
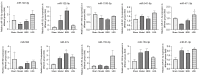
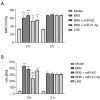
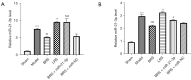
Results: After RT-qPCR verification, the variation trend of miR-21-3p was in line with expected trends. The mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) were decreased, and the lung injury and damage to the glycocalyx were all aggravated in the THS rats resuscitated with sodium bicarbonate Ringer's solution (BRS) or sodium lactate Ringer's solution (LRS). The expression of miR-21-3p was decreased in the THS rats resuscitated with BRS and increased in the THS rats resuscitated with LRS, and the upregulation of miR-21-3p further decreased the MAP and HR, and increased the levels of syndecan-1 (SDC-1), heparanase-1 (HPA1), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in the serum of the THS rats resuscitated with BRS. The upregulation of miR-21-3p also increased the expression of SDC-1, HPA1, β-catenin, matrix metallopeptidase (MMP)2, and MMP9, but decreased the expression of E-cadherin (E-cad) and activated the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway in the THS rats resuscitated with BRS and transfected with miR-21-3p compared to that of the THS rats resuscitated with BRS and transfected with miR-negative control (NC).
Conclusions: miR-21-3p promoted inflammation and glycocalyx damage by activating the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby aggravating the lung injury in the THS rats resuscitated with BRS.
Keywords: MiR-21-3p; lung injury; sodium bicarbonate Ringer’s solution (BRS); traumatic hemorrhagic shock (THS).
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-5148/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intraoperative Use of Sodium Bicarbonate Ringer's Solution Instead of Sodium Lactate Ringer's Solution to Reduce Endothelial Glycocalyx Degradation and Improve Postoperative Recovery During Cardiopulmonary Bypass Cardiac Surgery: A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Dec 10;18:5881-5893. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S501657. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39679133 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
EFFECT OF MIR-21-3P ON INTESTINAL INJURY IN RATS WITH TRAUMATIC HEMORRHAGIC SHOCK RESUSCITATED WITH THE SODIUM BICARBONATE RINGER'S SOLUTION.Shock. 2024 May 1;61(5):776-782. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002297. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Shock. 2024. PMID: 38517274
-
Effect of sodium bicarbonate Ringer's solution on lung injury in rats with traumatic hemorrhagic shock.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024 Jan;38(1):e23608. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23608. Epub 2023 Dec 12. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38084607
-
Observation on the effectiveness and safety of sodium bicarbonate Ringer's solution in the early resuscitation of traumatic hemorrhagic shock: a clinical single-center prospective randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2022 Sep 30;23(1):825. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06752-5. Trials. 2022. PMID: 36175936 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The conundrum of the definition of haemorrhagic shock: a pragmatic exploration based on a scoping review, experts' survey and a cohort analysis.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022 Dec;48(6):4639-4649. doi: 10.1007/s00068-022-01998-9. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2022. PMID: 35732811 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Intraoperative Use of Sodium Bicarbonate Ringer's Solution Instead of Sodium Lactate Ringer's Solution to Reduce Endothelial Glycocalyx Degradation and Improve Postoperative Recovery During Cardiopulmonary Bypass Cardiac Surgery: A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Dec 10;18:5881-5893. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S501657. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39679133 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
