Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) in Very Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (VLS-SCLC)
- PMID: 36661657
- PMCID: PMC9858162
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol30010008
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) in Very Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (VLS-SCLC)
Abstract
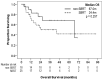
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive neuroendocrine tumour with metastatic propensity. Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) is an emerging therapeutic option for SCLC, despite limited supporting evidence. By evaluating the use of SBRT in very limited stage (VLS) SCLC at our institution, we aimed to contribute to the existing knowledge in this area while establishing a basis for further research. We performed a retrospective review of all cases of VLS-SCLC treated with SBRT between 2013 and 2020. Baseline demographics, diagnostic, and treatment information were collected. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS). We identified 46 patients with pathologically confirmed VLS-SCLC; 25 were treated with SBRT, and the remainder received either surgery, conventional radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or palliative-intent therapy. After a median follow-up of 23.7 months, 44% of the patients had died; the median OS was of 24.4 months for the SBRT cohort and 67.0 months for the curative intent non-SBRT cohort. The difference in disease recurrence and survival between cohorts was underpowered and not statistically significant. Higher baseline ECOG and comorbidity was noted in the SBRT cohort.
Keywords: SABR; SBRT; SCLC; limited stage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Outcomes Following Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) for Stage I Medically Inoperable Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Multi-Institutional Analysis From the RSSearch Patient Registry.Am J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul;42(7):602-606. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000561. Am J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31232723
-
Surgery and Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Stage I Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma: A 25-Year Experience.Clin Lung Cancer. 2024 Sep;25(6):537-549.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2024.06.001. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Clin Lung Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38926078
-
Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy versus conventionally fractionated radiation therapy for stage I small cell lung cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2019 Feb;131:145-149. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.12.006. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Radiother Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30773182
-
Stage-I small cell lung cancer: A new potential option for stereotactic ablative radiation therapy? A review of literature.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017 Apr;112:67-71. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.02.010. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28325266 Review.
-
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy in T1-2N0M0 small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Lung Cancer. 2021 Oct;160:179-186. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.07.007. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34330566
References
-
- Canadian Cancer Statistics Advisory Committee Lung Cancer Statistics. 2021. [(accessed on 17 December 2021)]. Available online: https://cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-types/lung/statistics.
-
- American Cancer Society What is Lung Cancer? 2019. [(accessed on 17 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/what-is.html.
-
- American Cancer Society Small Cell Lung Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention. 2016. [(accessed on 19 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/CRC/PDF/Public/8709.00.pdf.
-
- American Cancer Society Treating Small Cell Lung Cancer. 2021. [(accessed on 19 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/CRC/PDF/Public/8711.00.pdf.
-
- Micke P., Faldum A., Metz T., Beeh K.-M., Bittinger F., Hengstler J.G., Buhl R. Staging small cell lung cancer: Veterans Administration Lung Study Group versus International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer—what limits limited disease? Lung Cancer. 2002;37:271–276. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5002(02)00072-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical