Calcium-Polyphosphate Submicroparticles (CaPP) Improvement Effect of the Experimental Bleaching Gels' Chemical and Cellular-Viability Properties
- PMID: 36661808
- PMCID: PMC9857579
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9010042
Calcium-Polyphosphate Submicroparticles (CaPP) Improvement Effect of the Experimental Bleaching Gels' Chemical and Cellular-Viability Properties
Abstract
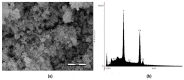
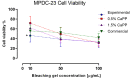
The aim of this research was to develop and characterize the chemical and cellular-viability properties of an experimental high-concentration bleaching gel (35 wt%-H2O2) containing calcium-polyphosphate particles (CaPP) at two concentrations (0.5 wt% and 1.5 wt%). The CaPP submicroparticles were synthesized by coprecipitation, keeping a Ca:P ratio of 2:1. The CaPP morphology, size, and chemical and crystal profiles were characterized through scanning and transmission electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray analysis, and X-ray diffraction, respectively. The assessed bleaching gels were experimental (without CaPP); 0.5% CaPP; 1.5% CaPP; and commercial. The gels’ pH values and H2O2 concentrations (iodometric titration) were determined. The odontoblast-like cell viability after a gel’s exposure was assessed by the MTT assay. The pH and H2O2 concentration were compared through a repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Tukey’s test and the cell viability through a one-way ANOVA and a Tukey’s test using a GraphPad Prism (α < 0.05). The CaPP particles were spherical (with Ca and P, 135.7 ± 80.95 nm size) and amorphous. The H2O2 concentration decreased in all groups after mixing (p < 0.001). The 0.5% CaPP resulted in more-stable pH levels and higher viability levels than the experimental one (p < 0.05). The successful incorporation of CaPP had a positive impact on the bleaching gel’s chemical and cellular-viability properties when compared to the experimental gel without these particles.
Keywords: bleaching; cell survival; hydrogen peroxide; pH; polyphosphates; submicroparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Barbosa J.G., Benetti F., Gallinari M.D.O., Carminatti M., da Silva A.B.D., Lopes I.N.I., Briso A.L.F., Cintra L.T.A. Bleaching gel mixed with MI Paste Plus reduces penetration of H2O2 and damage to pulp tissue and maintains bleaching effectiveness. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019;24:1299–1309. doi: 10.1007/s00784-019-03009-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tan L., Zhang P., Zhao X., Fan C., Zhang C., Yan Y., Von Gadow K. Analysing species abundance distribution patterns across sampling scales in three natural forests in Northeastern China. Iforest Biogeosci. For. 2020;13:482. doi: 10.3832/ifor3211-013. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

