Size-Resolved Redox Activity and Cytotoxicity of Water-Soluble Urban Atmospheric Particulate Matter: Assessing Contributions from Chemical Components
- PMID: 36668785
- PMCID: PMC9867266
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics11010059
Size-Resolved Redox Activity and Cytotoxicity of Water-Soluble Urban Atmospheric Particulate Matter: Assessing Contributions from Chemical Components
Abstract
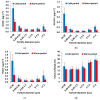
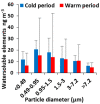
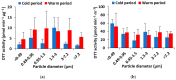
Throughout the cold and the warm periods of 2020, chemical and toxicological characterization of the water-soluble fraction of size segregated particulate matter (PM) (<0.49, 0.49−0.95, 0.95−1.5, 1.5−3.0, 3.0−7.2 and >7.2 μm) was conducted in the urban agglomeration of Thessaloniki, northern Greece. Chemical analysis of the water-soluble PM fraction included water-soluble organic carbon (WSOC), humic-like substances (HULIS), and trace elements (V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd and Pb). The bulk (sum of all size fractions) concentrations of HULIS were 2.5 ± 0.5 and 1.2 ± 0.3 μg m−3, for the cold and warm sampling periods, respectively with highest values in the <0.49 μm particle size fraction. The total HULIS-C/WSOC ratio ranged from 17 to 26% for all sampling periods, confirming that HULIS are a significant part of WSOC. The most abundant water-soluble metals were Fe, Zn, Cu, and Mn. The oxidative PM activity was measured abiotically using the dithiothreitol (DTT) assay. In vitro cytotoxic responses were investigated using mitochondrial dehydrogenase (MTT). A significant positive correlation was found between OPmDTT, WSOC, HULIS and the MTT cytotoxicity of PM. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) showed a good relationship between OPMDTT, HULIS and Cu.
Keywords: DTT assay; HULIS; MTT assay; WSOC; water soluble elements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Valavanidis A., Vlachogianni T., Fiotakis K., Loridas S. Pulmonary Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cancer: Respirable Particulate Matter, Fibrous Dusts and Ozone as Major Causes of Lung Carcinogenesis through Reactive Oxygen Species Mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2013;10:3886–3907. doi: 10.3390/ijerph10093886. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Janssen N.A.H., Strak M., Yang A., Hellack B., Kelly F.J., Kuhlbusch T.A.J., Harrison R.M., Brunekreef B., Cassee F.R., Steenhof M., et al. Associations between Three Specific A-Cellular Measures of the Oxidative Potential of Particulate Matter and Markers of Acute Airway and Nasal Inflammation in Healthy Volunteers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2015;72:49–56. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2014-102303. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- MIS-5033021/State Scholarships Foundation
- MIS-5033021/This research is co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Social Fund- ESF) through the Operational Programme «Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning» in the context of the project "Reinforcement of Postdoctoral Researc
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

