Bifunctional M13 Phage as Enzyme Container for the Reinforced Colorimetric-Photothermal Dual-Modal Sensing of Ochratoxin A
- PMID: 36668825
- PMCID: PMC9867381
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins15010005
Bifunctional M13 Phage as Enzyme Container for the Reinforced Colorimetric-Photothermal Dual-Modal Sensing of Ochratoxin A
Abstract
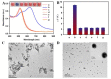
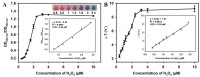
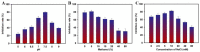
"Point of care" (POC) methods without expensive instruments and special technicians are greatly needed for high-throughput analysis of mycotoxins. In comparison, the most widely used screening method of the conventional enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) confronts low sensitivity and harmful competing antigens. Herein, we develop a plasmonic-photothermal ELISA that allows precise readout by color-temperature dual-modal signals based on enzymatic reaction-induced AuNP aggregation for highly sensitive detection of ochratoxin A (OTA). The bifunctional M13 phage carrying OTA that mimics the mimotope on the end of p3 proteins and abundant biotin molecules on the major p8 proteins is adopted as an eco-friendly competing antigen and enzyme container for amplifying the signal intensity. Under optimal conditions, both colorimetric and photothermal signals enable good dynamic linearity for quantitative OTA detection with the limits of detection at 12.1 and 8.6 pg mL-1, respectively. Additionally, the proposed ELISA was adapted to visual determination with a cutoff limit of 78 pg mL-1 according to a vivid color change from deep blue to red. The recoveries of OTA-spiked corn samples indicate the high accuracy and robustness of the proposed method. In conclusion, our proposed strategy provides a promising method for eco-friendly and sensitive POC screening of OTA. Moreover, it can be easily applied to other analytes by changing the involved specific mimotope sequence.
Keywords: AuNP aggregation; bifunctional M13 bacteriophage; enzyme container; ochratoxin A; plasmonic and photothermal ELISA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Luo S., Du H., Kebede H., Liu Y., Xing F. Contamination status of major mycotoxins in agricultural product and food stuff in Europe. Food Control. 2021;127:108120. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108120. - DOI
-
- Reddy K., Salleh B., Saad B., Abbas H., Abel C., Shier W. An overview of mycotoxin contamination in foods and its implications for human health. Toxin Rev. 2010;29:3–26. doi: 10.3109/15569541003598553. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

