The Bi-Functional Paxilline Enriched in Skin Secretion of Tree Frogs (Hyla japonica) Targets the KCNK18 and BKCa Channels
- PMID: 36668889
- PMCID: PMC9862588
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins15010070
The Bi-Functional Paxilline Enriched in Skin Secretion of Tree Frogs (Hyla japonica) Targets the KCNK18 and BKCa Channels
Abstract
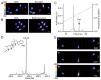
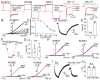
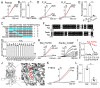
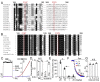
The skin secretion of tree frogs contains a vast array of bioactive chemicals for repelling predators, but their structural and functional diversity is not fully understood. Paxilline (PAX), a compound synthesized by Penicillium paxilli, has been known as a specific antagonist of large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ Channels (BKCa). Here, we report the presence of PAX in the secretions of tree frogs (Hyla japonica) and that this compound has a novel function of inhibiting the potassium channel subfamily K member 18 (KCNK18) channels of their predators. The PAX-induced KCNK18 inhibition is sufficient to evoke Ca2+ influx in charybdotoxin-insensitive DRG neurons of rats. By forming π-π stacking interactions, four phenylalanines located in the central pore of KCNK18 stabilize PAX to block the ion permeation. For PAX-mediated toxicity, our results from animal assays suggest that the inhibition of KCNK18 likely acts synergistically with that of BKCa to elicit tingling and buzzing sensations in predators or competitors. These results not only show the molecular mechanism of PAX-KCNK18 interaction, but also provide insights into the defensive effects of the enriched PAX.
Keywords: KCNK18; defensive strategy; paxilline; skin secretion; tree frogs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The functionally relevant site for paxilline inhibition of BK channels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jan 14;117(2):1021-1026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1912623117. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 31879339 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental diabetes mellitus down-regulates large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cerebral artery smooth muscle and alters functional conductance.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2010 May;7(2):75-84. doi: 10.2174/156720210791184925. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2010. PMID: 20334613
-
Flavonoid quercetin abolish paxilline inhibition of the mitochondrial BKCa channel.Mitochondrion. 2022 Jul;65:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2022.04.005. Epub 2022 Apr 30. Mitochondrion. 2022. PMID: 35504559
-
Paxilline inhibition of the alpha-subunit of the high-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel.Neuropharmacology. 1996;35(7):963-8. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(96)00137-2. Neuropharmacology. 1996. PMID: 8938726
-
Potassium channel openers as potential therapeutic weapons in ion channel disease.Kidney Int. 2000 Mar;57(3):838-45. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2000.00923.x. Kidney Int. 2000. PMID: 10720937 Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Research on Animal Venoms in China.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Apr 6;15(4):272. doi: 10.3390/toxins15040272. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37104210 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

