Glucokinase Inhibition: A Novel Treatment for Diabetes?
- PMID: 36669001
- PMCID: PMC9871191
- DOI: 10.2337/db22-0731
Glucokinase Inhibition: A Novel Treatment for Diabetes?
Abstract
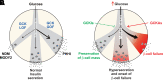
Chronic hyperglycemia increases pancreatic β-cell metabolic activity, contributing to glucotoxicity-induced β-cell failure and loss of functional β-cell mass, potentially in multiple forms of diabetes. In this perspective we discuss the novel paradoxical and counterintuitive concept of inhibiting glycolysis, particularly by targeted inhibition of glucokinase, the first enzyme in glycolysis, as an approach to maintaining glucose sensing and preserving functional β-cell mass, thereby improving insulin secretion, in the treatment of diabetes.
© 2023 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Kahn SE. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2003;46:3–19 - PubMed
-
- Rahier J, Guiot Y, Goebbels RM, Sempoux C, Henquin JC. Pancreatic beta-cell mass in European subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2008;10(Suppl. 4):32–42 - PubMed
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003;52:102–110 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

