Mammalian life depends on two distinct pathways of DNA damage tolerance
- PMID: 36669105
- PMCID: PMC9942833
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2216055120
Mammalian life depends on two distinct pathways of DNA damage tolerance
Abstract
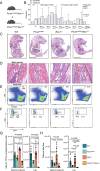
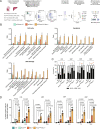
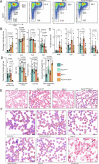
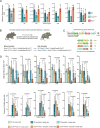
DNA damage threatens genomic integrity and instigates stem cell failure. To bypass genotoxic lesions during replication, cells employ DNA damage tolerance (DDT), which is regulated via PCNA ubiquitination and REV1. DDT is conserved in all domains of life, yet its relevance in mammals remains unclear. Here, we show that inactivation of both PCNA-ubiquitination and REV1 results in embryonic and adult lethality, and the accumulation of DNA damage in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) that ultimately resulted in their depletion. Our results reveal the crucial relevance of DDT in the maintenance of stem cell compartments and mammalian life in unperturbed conditions.
Keywords: DNA damage response (DDR); DNA damage tolerance (DDT); embryonic lethality; erythropoiesis; hematopoietic stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Division of labor within the DNA damage tolerance system reveals non-epistatic and clinically actionable targets for precision cancer medicine.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jul 22;50(13):7420-7435. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac545. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35819193 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-damage tolerance through PCNA ubiquitination and sumoylation.Biochem J. 2020 Jul 31;477(14):2655-2677. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20190579. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32726436 Review.
-
DNA damage tolerance in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Aug 15;114(33):E6875-E6883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706508114. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28761001 Free PMC article.
-
Relevance of simultaneous mono-ubiquitinations of multiple units of PCNA homo-trimers in DNA damage tolerance.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 18;10(2):e0118775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118775. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25692884 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal regulation of PCNA ubiquitination in damage tolerance pathways.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Oct;54(5):418-442. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2019.1687420. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31736364 Review.
Cited by
-
PRIMPOL ensures robust handoff between on-the-fly and post-replicative DNA lesion bypass.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 11;52(1):243-258. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1054. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 37971291 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical and Non-Canonical Roles of Human DNA Polymerase η.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;15(10):1271. doi: 10.3390/genes15101271. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular dependencies and genomic consequences of a global DNA damage tolerance defect.Genome Biol. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):323. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03451-z. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 39741332 Free PMC article.
-
Replication stress responses in human lymphocytes change sex-specifically during aging.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jun 6;53(11):gkaf498. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf498. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40530696 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

