DeepFundus: A flow-cytometry-like image quality classifier for boosting the whole life cycle of medical artificial intelligence
- PMID: 36669488
- PMCID: PMC9975093
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100912
DeepFundus: A flow-cytometry-like image quality classifier for boosting the whole life cycle of medical artificial intelligence
Abstract
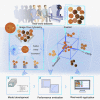
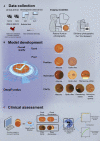
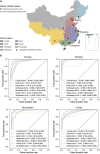
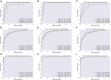
Medical artificial intelligence (AI) has been moving from the research phase to clinical implementation. However, most AI-based models are mainly built using high-quality images preprocessed in the laboratory, which is not representative of real-world settings. This dataset bias proves a major driver of AI system dysfunction. Inspired by the design of flow cytometry, DeepFundus, a deep-learning-based fundus image classifier, is developed to provide automated and multidimensional image sorting to address this data quality gap. DeepFundus achieves areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUCs) over 0.9 in image classification concerning overall quality, clinical quality factors, and structural quality analysis on both the internal test and national validation datasets. Additionally, DeepFundus can be integrated into both model development and clinical application of AI diagnostics to significantly enhance model performance for detecting multiple retinopathies. DeepFundus can be used to construct a data-driven paradigm for improving the entire life cycle of medical AI practice.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; image quality; retinal diseases.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Solving data quality issues of fundus images in real-world settings by ophthalmic AI.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Feb 21;4(2):100951. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.100951. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 36812885 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a deep learning-based image eligibility verification system for detecting and filtering out ineligible fundus images: A multicentre study.Int J Med Inform. 2021 Mar;147:104363. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104363. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Int J Med Inform. 2021. PMID: 33388480
-
Application of Comprehensive Artificial intelligence Retinal Expert (CARE) system: a national real-world evidence study.Lancet Digit Health. 2021 Aug;3(8):e486-e495. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(21)00086-8. Lancet Digit Health. 2021. PMID: 34325853
-
What Are the Applications and Limitations of Artificial Intelligence for Fracture Detection and Classification in Orthopaedic Trauma Imaging? A Systematic Review.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Nov;477(11):2482-2491. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000848. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 31283727 Free PMC article.
-
Key Principles of Clinical Validation, Device Approval, and Insurance Coverage Decisions of Artificial Intelligence.Korean J Radiol. 2021 Mar;22(3):442-453. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2021.0048. Korean J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33629545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence in ophthalmology: The path to the real-world clinic.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Jul 18;4(7):101095. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101095. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 37385253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic Retinopathy Assessment through Multitask Learning Approach on Heterogeneous Fundus Image Datasets.Ophthalmol Sci. 2025 Mar 11;5(5):100755. doi: 10.1016/j.xops.2025.100755. eCollection 2025 Sep-Oct. Ophthalmol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520476 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of a deep learning system for screening real-world multiple abnormal findings based on ultra-widefield fundus images.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 3;12:1584378. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1584378. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40529144 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the ophthalmic AI assessment with a fundus image quality classifier using local and global attention mechanisms.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 7;11:1418048. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1418048. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39175821 Free PMC article.
-
COph100: A comprehensive fundus image registration dataset from infants constituting the "RIDIRP" database.Sci Data. 2025 Jan 17;12(1):99. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04426-w. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 39824846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beede E., Baylor E., Hersch F., Iurchenko A., Wilcox L., Ruamviboonsuk P., Vardoulakis L.M. 2020. A Human-Centered Evaluation of a Deep Learning System Deployed in Clinics for the Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy; pp. 1–12.
-
- Lin H., Li R., Liu Z., Chen J., Yang Y., Chen H., Lin Z., Lai W., Long E., Wu X., et al. Diagnostic efficacy and therapeutic decision-making capacity of an artificial intelligence platform for childhood cataracts in eye clinics: a multicentre randomized controlled trial. EClinicalMedicine. 2019;9:52–59. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2019.03.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

