Development of tailored splice-switching oligonucleotides for progressive brain disorders in Europe: development, regulation, and implementation considerations
- PMID: 36669889
- PMCID: PMC10019362
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.079540.122
Development of tailored splice-switching oligonucleotides for progressive brain disorders in Europe: development, regulation, and implementation considerations
Abstract
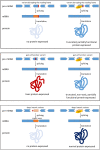
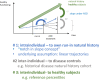
Splice-modulating antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) offer treatment options for rare neurological diseases, including those with very rare mutations, where patient-specific, individualized ASOs have to be developed. Inspired by the development of milasen, the 1 Mutation 1 Medicine (1M1M) and Dutch Center for RNA Therapeutics (DCRT) aim to develop patient-specific ASOs and treat eligible patients within Europe and the Netherlands, respectively. Treatment will be provided under a named patient setting. Our initiatives benefited from regulatory advice from the European Medicines Agency (EMA) with regard to preclinical proof-of-concept studies, safety studies, compounding and measuring benefit and safety in treated patients. We here outline the most important considerations from these interactions and how we implemented this advice into our plan to develop and treat eligible patients within Europe.
Keywords: Europe; N = 1; antisense oligonucleotides; regulators; treatment.
© 2023 Aartsma-Rus et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
References
-
- Aartsma-Rus A, Dooms M, Le Cam Y. 2021. Orphan medicine incentives: how to address the unmet needs of rare disease patients by optimizing the European orphan medicinal product landscape guiding principles and policy proposals by the European expert group for orphan drug incentives (OD Expert Group). Front Pharmacol 12: 744532. 10.3389/fphar.2021.744532 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
