Integrative genetic analysis illuminates ALS heritability and identifies risk genes
- PMID: 36670122
- PMCID: PMC9860017
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35724-1
Integrative genetic analysis illuminates ALS heritability and identifies risk genes
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Integrative genetic analysis illuminates ALS heritability and identifies risk genes.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 4;14(1):8026. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43710-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38049418 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
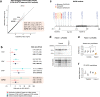
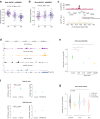
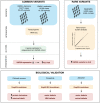
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) has substantial heritability, in part shared with fronto-temporal dementia (FTD). We show that ALS heritability is enriched in splicing variants and in binding sites of 6 RNA-binding proteins including TDP-43 and FUS. A transcriptome wide association study (TWAS) identified 6 loci associated with ALS, including in NUP50 encoding for the nucleopore basket protein NUP50. Independently, rare variants in NUP50 were associated with ALS risk (P = 3.71.10-03; odds ratio = 3.29; 95%CI, 1.37 to 7.87) in a cohort of 9,390 ALS/FTD patients and 4,594 controls. Cells from one patient carrying a NUP50 frameshift mutation displayed a decreased level of NUP50. Loss of NUP50 leads to death of cultured neurons, and motor defects in Drosophila and zebrafish. Thus, our study identifies alterations in splicing in neurons as critical in ALS and provides genetic evidence linking nuclear pore defects to ALS.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
J.H.V. reports having sponsored research agreements with Biogen. L.D. reports having sponsored research agreements with Inflectis Bioscience and Cytokinetics. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Gregory, J. M., Fagegaltier, D., Phatnani, H. & Harms, M. B. Genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr. Genet. Med. Rep.8, 121–131 (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

