Prevalence, predictors and pregnancy outcomes of unprescribed and herbal medicine use in Ibadan, Nigeria
- PMID: 36670404
- PMCID: PMC9854176
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-023-03838-8
Prevalence, predictors and pregnancy outcomes of unprescribed and herbal medicine use in Ibadan, Nigeria
Abstract
Background: Unprescribed and herbal medicines use among pregnant women is a public health concern in low and middle-income countries because of the potential teratogenic effects, insufficient safety and weak drug regulatory systems. Unprescribed and herbal medicines are common among pregnant women in Nigeria, and only a few researchers have documented the prevalence and the risk factors. However, evidence on the associated pregnancy outcomes is still lacking. We assessed the prevalence, predictors and pregnancy outcomes of unprescribed and herbal medicines use among pregnant women in Ibadan, Nigeria.
Methods: This study was a component of the Ibadan Pregnancy Cohort Study, a prospective cohort study, among pregnant women in Ibadan, Nigeria, who were enrolled at ≤ 20 weeks gestation at their first antenatal visit and followed up till delivery. In all, 571 women participated in the maternal drug use assessment during the third trimester using a pretested interviewer-administered questionnaire. The primary outcomes were unprescribed and herbal medicines use and pregnancy outcomes, secondary outcomes, were abstracted from medical records. The predictors assessed included sociodemographic, obstetric, antenatal care utilization, and lifestyle characteristics. Bi-variate logistic and Poisson regression analyses were used to evaluate the predictors and relative risk for the pregnancy outcomes of unprescribed and herbal medicines at 5% significance.
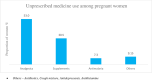
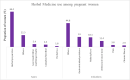
Results: The prevalence of unprescribed and herbal medicine use was 31.9% and 21.7%, respectively. On bivariate analysis, the significant predictors of unprescribed medicine (which were protective) were tertiary education, increasing income, adequate antenatal care (≥ 4 visits), and at least two doses of sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine. However, high parity and having an antenatal admission increased the risk. However, after adjusting for confounders, the significant factors associated with unprescribed medicines were; tertiary education (AOR) = 0.23; 95% CI: (0.06 - 0.95); p-value: 0.043] and obtaining at least two doses of sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine [AOR = 0.33; 95% CI: (0.29 - 3.60); p-value: 0.048]. For herbal medicines, the predictors were similar to unprescribed drugs. However, after adjusting for confounders, none was significant for herbal medicines. Unprescribed and herbal medicines were not significantly associated with pregnancy outcomes.
Conclusions: Unprescribed and herbal medicines use were common among pregnant women in Ibadan, Nigeria, particularly among women with low economic status and those with poor utilization of antenatal care services. These significant predictors can be targeted for public health intervention. Specifically, health education that discourages the use of unprescribed and herbal medications to pregnant women during antenatal care.
Keywords: Herbal medicines; Nigeria; Predictors; Pregnancy outcomes; Prevalence; Unprescribed medicines.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources