Anti-Osteoarthritic Effects of Prunella Vulgaris and Gentiana Lutea In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 36670908
- PMCID: PMC9854930
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12010047
Anti-Osteoarthritic Effects of Prunella Vulgaris and Gentiana Lutea In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
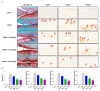
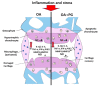
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive destruction of articular cartilage with severe symptoms, including pain and stiffness. We investigated the anti-osteoarthritic effects of Prunella vulgaris (PV) and Gentiana lutea (GL) extract in primary cultured chondrocytes RAW 264.7 cells in vitro and destabilization of the medial meniscus (DMM)-induced OA mice in vivo. Primary chondrocytes were induced with IL-1β, and RAW 264.7 cells were treated with LPS and co-incubated with either individual extracts of PV and GL or different ratios of PV and GL mixture. For the OA animal model, the medial meniscus (DMM) was destabilized in 9-week-old male C57BL/6 mice. Treatment of individual PV and GL and combination of PV and GL extracts inhibited the mRNA expression level of COX2 in chondrocytes and RAW 264.7 cells. The optimized inhibitory effect was attained with a PV and GL combination at an 8:2 ratio (PG) without cytotoxic effects. PG extracts prevented the expression of catabolic factors (COX2, Mmp3, Mmp9, and Mmp13) and inflammatory mediator levels (PGE2 and collagenase). In addition, PG decreased subchondral sclerosis and increased BMD in the subchondral region of DMM-induced OA mice with protection of articular cartilage destruction by inhibiting inflammatory processes. This study suggests that PG may be an alternative medicinal herb for treatment of OA.
Keywords: Gentiana lutea; Prunella vulgaris; anti-inflammatory effect; destabilization of medial meniscus; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
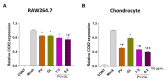

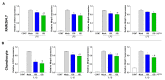

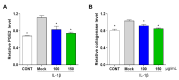
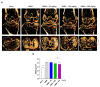
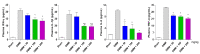
Similar articles
-
Antiosteoarthritic Effect of Morroniside in Chondrocyte Inflammation and Destabilization of Medial Meniscus-Induced Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 15;22(6):2987. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062987. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804203 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 plays an essential role in hypoxia-inducible factor 2α-induced experimental osteoarthritic cartilage destruction in mice.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Sep;63(9):2732-43. doi: 10.1002/art.30451. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21590680
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5 governs Wnt-mediated osteoarthritic cartilage destruction.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Jan 31;16(1):R37. doi: 10.1186/ar4466. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24479426 Free PMC article.
-
18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in mouse chondrocytes and prevents osteoarthritic progression by activating Nrf2.Food Funct. 2021 Sep 20;12(18):8399-8410. doi: 10.1039/d1fo01379c. Food Funct. 2021. PMID: 34369548
-
Prunella vulgaris L.: An Updated Overview of Botany, Chemical Composition, Extraction Methods, and Biological Activities.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 4;16(8):1106. doi: 10.3390/ph16081106. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631021 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Analysis and Antioxidant Effects of Prunella vulgaris in Experimental Acute Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 29;25(9):4843. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094843. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732062 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa) Leaf By-Products: Bioactive Compounds, Anti-Inflammatory Properties, and Potential Health Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 10;26(2):548. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020548. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859264 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- HR22C1734/Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institution (KHIDI)
- HR21C1003/Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institution (KHIDI)
- R&D, grant number: S2910765/Regional Specialized Industry Development Program
- NRF2021M3H1A104892211/Korea Initiative for Fostering University of Research and Innovation Program of the National Re-search Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

