Salinity Stress Ameliorates Pigments, Minerals, Polyphenolic Profiles, and Antiradical Capacity in Lalshak
- PMID: 36671036
- PMCID: PMC9855230
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12010173
Salinity Stress Ameliorates Pigments, Minerals, Polyphenolic Profiles, and Antiradical Capacity in Lalshak
Abstract
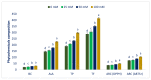
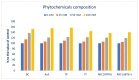
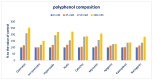
Previous studies have shown that salinity eustress enhances the nutritional and bioactive compounds and antiradical capacity (ARC) of vegetables and increases the food values for nourishing human diets. Amaranth is a salinity-resistant, rapidly grown C4 leafy vegetable with diverse variability and usage. It has a high possibility to enhance nutritional and bioactive compounds and ARC by the application of salinity eustress. Hence, the present study aimed to evaluate the effects of sodium chloride stress response in a selected Lalshak (A. gangeticus) genotype on minerals, ascorbic acid (AsA), Folin−Ciocalteu reducing capacity, beta-carotene (BC), total flavonoids (TF), pigments, polyphenolic profiles, and ARC. A high-yield, high-ARC genotype (LS6) was grown under conditions of 0, 25, 50, and 100 mM sodium chloride in four replicates following a block design with complete randomization. We recognized nine copious polyphenolic compounds in this accession for the first time. Minerals, Folin−Ciocalteu reducing capacity, AsA, BC, pigments, polyphenolic profiles, and ARC of Lalshak were augmented progressively in the order: 0 < 25 < 50 < 100 mM sodium chloride. At 50 mM and 100 mM salt concentrations, minerals, AsA, Folin−Ciocalteu reducing capacity, BC, TF, pigments, polyphenolic profiles, and ARC of Lalshak were much greater than those of the control. Lalshak could be used as valuable food for human diets as a potent antioxidant. Sodium chloride-enriched Lalshak provided outstanding quality to the final product in terms of minerals, AsA, Folin−Ciocalteu reducing capacity, BC, TF, pigments, polyphenolic profiles, and ARC. We can cultivate it as a promising alternative crop in salinity-prone areas of the world.
Keywords: ABTS+; DPPH; HPLC–UV; antiradical capacity; ascorbic acid; beta-carotene; color attributes and pigment; minerals; polyphenolic profiles; salinity stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Salt Eustress Induction in Red Amaranth (Amaranthus gangeticus) Augments Nutritional, Phenolic Acids and Antiradical Potential of Leaves.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Dec 9;11(12):2434. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122434. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552642 Free PMC article.
-
Salinity stress enhances color parameters, bioactive leaf pigments, vitamins, polyphenols, flavonoids and antioxidant activity in selected Amaranthus leafy vegetables.J Sci Food Agric. 2019 Mar 30;99(5):2275-2284. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9423. Epub 2018 Nov 28. J Sci Food Agric. 2019. PMID: 30324618
-
Salinity stress accelerates nutrients, dietary fiber, minerals, phytochemicals and antioxidant activity in Amaranthus tricolor leaves.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 1;13(11):e0206388. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206388. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30383779 Free PMC article.
-
Augmentation of leaf color parameters, pigments, vitamins, phenolic acids, flavonoids and antioxidant activity in selected Amaranthus tricolor under salinity stress.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 17;8(1):12349. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30897-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30120319 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction, chemical characterization and biological activity determination of broccoli health promoting compounds.J Chromatogr A. 2013 Oct 25;1313:78-95. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.07.051. Epub 2013 Jul 16. J Chromatogr A. 2013. PMID: 23899380 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Carbon Nanodots and Manganese Ferrite (MnFe2O4) Nanoparticles in Stimulating Growth and Antioxidant Activity in Drought-Stressed Maize Inbred Lines.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;12(16):2922. doi: 10.3390/plants12162922. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631134 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of household processing on nutritional and antinutritional composition, mineral-mineral ratios, and functional properties of Colocasia leaves.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 14;9(6):e17137. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17137. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37383195 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Some Fruit Quality Parameters of Selected 12 Mandarin Genotypes from Black Sea Region in Turkey.ACS Omega. 2023 May 23;8(22):19719-19727. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01364. eCollection 2023 Jun 6. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37305317 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Salinity in the Irrigation of a Wild Underutilized Leafy Vegetable, Sonchus oleraceus L.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 4;13(11):1552. doi: 10.3390/plants13111552. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891360 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of foliar spray and post-harvest treatments on head yield, shelf-life, and physicochemical qualities of broccoli.Front Nutr. 2023 Apr 17;10:1057084. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1057084. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37139458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stintzing F.C., Carle R. Betalains—Emerging prospects for food scientists. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007;18:514–525. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2007.04.012. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

