Antifungal Activities of Compounds Produced by Newly Isolated Acrocarpospora Strains
- PMID: 36671296
- PMCID: PMC9854854
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics12010095
Antifungal Activities of Compounds Produced by Newly Isolated Acrocarpospora Strains
Abstract
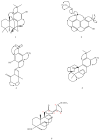
In our continued search for bioactive metabolites from cultures of rare Actinobacteria resources from all over Taiwan and various natural ecological environments, an active antimicrobial strain of Acrocarpospora punica 04107M was collected in Taitung County in Taiwan and prepared from soil. The bioassay-guided fractionation of the BuOH extract of a culture broth from A. punica 04107M led to the isolation of five previously undescribed compounds: Acrocarposporins A−E (Compounds 1−5). All the constituents were confirmed by HRESIMS and 1D- and 2D-NMR spectroscopy. Their antifungal activity was also evaluated. Our results showed that four constituents (Compounds 1, 2, 4, and 5) possessed mild antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger, Penicillium italicum, Candida albicans, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It is worth mentioning that the chemical composition of Acrocarpospora punica 04107M has never been studied. This is the first report on diterpenoid metabolites from the genus Acrocarpospora.
Keywords: Acrocarpospora punica 04107M; Streptosporangiaceae; antifungal activities; diterpenoid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Barman D., Dkhar M.S. Seasonal variation influence endophytic Actinobacterial communities of medicinal plants from tropical deciduous forest of Meghalaya and characterization of their plant growth-promoting potentials. Curr. Microbiol. 2020;77:1689–1698. doi: 10.1007/s00284-020-01988-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nguyen H.T., Pokhrel A.R., Nguyen C.T., Pham V.T.T., Dhakal D., Lim H.N., Jung H.J., Kim T.S., Yamaguchi T., Sohng J.K. Streptomyces Sp. VN1, a Producer of Diverse Metabolites Including Non-Natural Furan-Type Anticancer Compound. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:1756. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58623-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

