De-Aliasing and Accelerated Sparse Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction Using Fully Dense CNN with Attention Gates
- PMID: 36671594
- PMCID: PMC9854709
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10010022
De-Aliasing and Accelerated Sparse Magnetic Resonance Image Reconstruction Using Fully Dense CNN with Attention Gates
Abstract
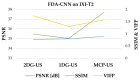
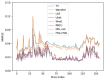
When sparsely sampled data are used to accelerate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), conventional reconstruction approaches produce significant artifacts that obscure the content of the image. To remove aliasing artifacts, we propose an advanced convolutional neural network (CNN) called fully dense attention CNN (FDA-CNN). We updated the Unet model with the fully dense connectivity and attention mechanism for MRI reconstruction. The main benefit of FDA-CNN is that an attention gate in each decoder layer increases the learning process by focusing on the relevant image features and provides a better generalization of the network by reducing irrelevant activations. Moreover, densely interconnected convolutional layers reuse the feature maps and prevent the vanishing gradient problem. Additionally, we also implement a new, proficient under-sampling pattern in the phase direction that takes low and high frequencies from the k-space both randomly and non-randomly. The performance of FDA-CNN was evaluated quantitatively and qualitatively with three different sub-sampling masks and datasets. Compared with five current deep learning-based and two compressed sensing MRI reconstruction techniques, the proposed method performed better as it reconstructed smoother and brighter images. Furthermore, FDA-CNN improved the mean PSNR by 2 dB, SSIM by 0.35, and VIFP by 0.37 compared with Unet for the acceleration factor of 5.
Keywords: MRI reconstruction; aliasing artifacts; attention gate; deep learning; fully dense network.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


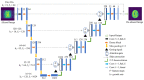


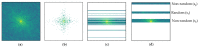
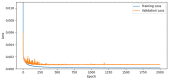
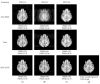




References
-
- Brown R.W., Cheng Y.-C.N., Haacke E.M., Thompson M.R., Venkatesan R. Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Physical Principles and Sequence Design. 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons Ltd; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2014.
-
- Cercignani M., Dowell N.G., Paul S. Tofts Quantitative MRI of the Brain: Principles of Physical Measurement. Volume 15. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2018.
-
- Muckley M.J., Riemenschneider B., Radmanesh A., Kim S., Jeong G., Ko J., Jun Y., Shin H., Hwang D., Mostapha M., et al. Results of the 2020 fastMRI challenge for machine learning MR image reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2021;40:2306–2317. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2021.3075856. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Por E., van Kooten M., Sarkovic V. Nyquist–Shannon Sampling Theorem. Leiden University; Leiden, The Netherlands: 2019.
-
- Schoenberg S.O., Dietrich O., Reiser M.F. Parallel Imaging in Clinical MR Applications. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2007. (Medical Radiology).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

