Long-Term Seizure Outcomes and Predictors in Patients with Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumors Associated with Epilepsy
- PMID: 36672006
- PMCID: PMC9856460
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13010024
Long-Term Seizure Outcomes and Predictors in Patients with Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumors Associated with Epilepsy
Abstract
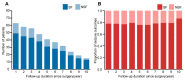
To determine the predictors and the long-term outcomes of patients with seizures following surgery for dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors (DNTs); Methods: Clinical data were collected from medical records of consecutive patients of the Department of Neurosurgery of Sanbo Brain Hospital of Capital Medical University with a pathological diagnosis of DNT and who underwent surgery from January 2008 to July 2021. All patients were followed up after surgery for at least one year. We estimated the cumulative rate of seizure recurrence-free and generated survival curves. A log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test and a Cox proportional hazard model were performed for univariate and multivariate analysis to analyze influential predictors; Results: 63 patients (33 males and 30 females) were included in this study. At the final follow-up, 49 patients (77.8%) were seizure-free. The cumulative rate of seizure recurrence-free was 82.5% (95% confidence interval (CI) 71.8-91.3%), 79.0% (95% CI 67.8-88.6%) and 76.5% (95% CI 64.8-87.0%) at 2, 5, and 10 years, respectively. The mean time for seizure recurrence-free was 6.892 ± 0.501 years (95% CI 5.91-7.87). Gross total removal of the tumor and a short epilepsy duration were significant predictors of seizure freedom. Younger age of seizure onset, bilateral interictal epileptiform discharges, and MRI type 3 tumors were risk factors for poor prognosis; Conclusions: A favorable long-term seizure outcome was observed for patients with DNT after surgical resection. Predictor analysis could effectively guide the clinical work and evaluate the prognosis of patients with DNT associated with epilepsy.
Keywords: dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors; epilepsy; prognosis; seizure outcome; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors in childhood: long-term outcome and prognostic features.Neurology. 2004 Jun 22;62(12):2270-6. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000130495.69512.6f. Neurology. 2004. PMID: 15210893
-
Factors associated with prognosis of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors patients after surgical resection: a retrospective observational study.Br J Neurosurg. 2024 Apr;38(2):372-377. doi: 10.1080/02688697.2021.1878107. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Br J Neurosurg. 2024. PMID: 33527856
-
Predictors and Long-term Outcome of Resective Epilepsy Surgery in Patients with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: A Single-centre Retrospective Cohort Study.Seizure. 2021 May;88:45-52. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2021.03.022. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Seizure. 2021. PMID: 33812307
-
Review of seizure outcomes after surgical resection of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors.J Neurooncol. 2016 Jan;126(1):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-1961-4. Epub 2015 Oct 29. J Neurooncol. 2016. PMID: 26514362 Review.
-
Simple and complex dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors (DNT) variants: clinical profile, MRI, and histopathology.Neuroradiology. 2009 Jul;51(7):433-43. doi: 10.1007/s00234-009-0511-1. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Neuroradiology. 2009. PMID: 19242688 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain tumor-related epilepsy management: A Society for Neuro-oncology (SNO) consensus review on current management.Neuro Oncol. 2024 Jan 5;26(1):7-24. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noad154. Neuro Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37699031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Wesseling P., Brat D.J., Cree I.A., Figarella-Branger D., Hawkins C., Ng H.K., Pfister S.M., Reifenberger G., et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-Oncol. 2021;23:1231–1251. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noab106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

