Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Lenvatinib Therapy in a Patient with Olfactory Neuroblastoma
- PMID: 36672016
- PMCID: PMC9856907
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13010033
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome after Lenvatinib Therapy in a Patient with Olfactory Neuroblastoma
Abstract
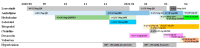
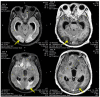
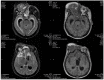
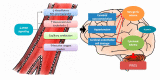
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a rare but severe neurological syndrome that may stem from the use of some medications. Although its mechanism is not well-known, hypertension and endothelial dysfunction have been mentioned in previous literature as being related. Lenvatinib serves as a neoplastic agent that inhibits the tyrosine kinase of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR). VEGFR inhibitors result in endothelial dysfunction and consequent hypertension by nitric oxide pathway suppression and endothelin (ET)-1 stimulation. We hypothesized that VEGFR inhibitors would cause PRES. Herein, we report the case of a 40-year-old man with olfactory neuroblastoma who developed PRES while undergoing treatment with lenvatinib, 7 months after initiation. The symptoms included loss of consciousness and seizures. Fortunately, the symptoms and presence of PRES in imaging resolved, 7 days and 1 month, respectively, after cessation of lenvatinib.
Keywords: lenvatinib; olfactory neuroblastoma; posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Buchhanolla P., Bir S., Angelette A., Lewis A., Kandregula S., Guthikonda B., Javalkar V., Chernyshev O., Kelley R. Determination of Prevalence of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) and Its Association with Cerebral Infarction, and Outcome in the Nationwide Inpatient Sample, 2016–2018 (P16-10.002) Neurology. 2022;98((Suppl. 18)):3555.
-
- Lenvima (lenvatinib) Product Monograph. Eisai Co., Ltd.; Mississauga, ON, Canada: 2020. [(accessed on 7 November 2022)]. Available online: https://ca.eisai.com/-/media/Files/CanadaEisai/LENVIMA-Product-Monograph....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

