In Silico Structural Analysis Predicting the Pathogenicity of PLP1 Mutations in Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 36672024
- PMCID: PMC9856082
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13010042
In Silico Structural Analysis Predicting the Pathogenicity of PLP1 Mutations in Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
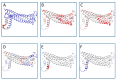
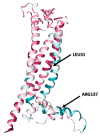
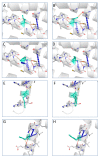
The X chromosome gene PLP1 encodes myelin proteolipid protein (PLP), the most prevalent protein in the myelin sheath surrounding the central nervous system. X-linked dysmyelinating disorders such as Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD) or spastic paraplegia type 2 (SPG2) are typically caused by point mutations in PLP1. Nevertheless, numerous case reports have shown individuals with PLP1 missense point mutations which also presented clinical symptoms and indications that were consistent with the diagnostic criteria of multiple sclerosis (MS), a disabling disease of the brain and spinal cord with no current cure. Computational structural biology methods were used to assess the impact of these mutations on the stability and flexibility of PLP structure in order to determine the role of PLP1 mutations in MS pathogenicity. The analysis showed that most of the variants can alter the functionality of the protein structure such as R137W variants which results in loss of helix and H140Y which alters the ordered protein interface. In silico genomic methods were also performed to predict the significance of these mutations associated with impairments in protein functionality and could suggest a better definition for therapeutic strategies and clinical application in MS patients.
Keywords: functional analysis; multiple sclerosis; myelin proteolipid protein; protein structure prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PLP1 Mutations in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis: Identification of a New Mutation and Potential Pathogenicity of the Mutations.J Clin Med. 2018 Oct 11;7(10):342. doi: 10.3390/jcm7100342. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30314286 Free PMC article.
-
The spectrum of PLP1 gene mutations in patients with the classical form of the Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease.Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2013 Oct-Dec;17(4):293-300. Med Wieku Rozwoj. 2013. PMID: 24519770
-
PLP1 splicing abnormalities identified in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease and SPG2 fibroblasts are associated with different types of mutations.Hum Mutat. 2008 Aug;29(8):1028-36. doi: 10.1002/humu.20758. Hum Mutat. 2008. PMID: 18470932
-
PLP1-related inherited dysmyelinating disorders: Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease and spastic paraplegia type 2.Neurogenetics. 2005 Feb;6(1):1-16. doi: 10.1007/s10048-004-0207-y. Epub 2004 Dec 31. Neurogenetics. 2005. PMID: 15627202 Review.
-
The molecular and cellular defects underlying Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008 May 19;10:e14. doi: 10.1017/S1462399408000677. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 18485258 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges and Perspectives of Neurological Disorders.Brain Sci. 2023 Apr 18;13(4):676. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13040676. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37190641 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

