Decreased Brain Structural Network Connectivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Novel Fractal Dimension Analysis
- PMID: 36672073
- PMCID: PMC9856782
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13010093
Decreased Brain Structural Network Connectivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Novel Fractal Dimension Analysis
Abstract
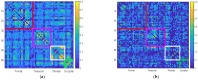
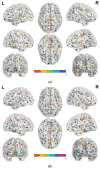
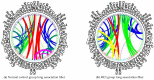
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is widely regarded to be the intermediate stage to Alzheimer's disease. Cerebral morphological alteration in cortical subregions can provide an accurate predictor for early recognition of MCI. Thirty patients with MCI and thirty healthy control subjects participated in this study. The Desikan-Killiany cortical atlas was applied to segment participants' cerebral cortex into 68 subregions. A complexity measure termed fractal dimension (FD) was applied to assess morphological changes in cortical subregions of participants. The MCI group revealed significantly decreased FD values in the bilateral temporal lobes, right parietal lobe including the medial temporal, fusiform, para hippocampal, and also the orbitofrontal lobes. We further proposed a novel FD-based brain structural network to compare network parameters, including intra- and inter-lobular connectivity between groups. The control group had five modules, and the MCI group had six modules in their brain networks. The MCI group demonstrated shrinkage of modular sizes with fewer components integrated, and significantly decreased global modularity in the brain network. The MCI group had lower intra- and inter-lobular connectivity in all lobes. Between cerebral lobes, the MCI patients may maintain nodal connections between both hemispheres to reduce connectivity loss in the lateral hemispheres. The method and results presented in this study could be a suitable tool for early detection of MCI.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; MCI; brain structural network; cognitive function; fractal dimension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no any conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Using Fractal Dimension Analysis with the Desikan-Killiany Atlas to Assess the Effects of Normal Aging on Subregional Cortex Alterations in Adulthood.Brain Sci. 2021 Jan 14;11(1):107. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11010107. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33466961 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring cortical morphology biomarkers of amnesic mild cognitive impairment using novel fractal dimension-based structural MRI analysis.Eur J Neurosci. 2024 Nov;60(9):6254-6266. doi: 10.1111/ejn.16557. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Eur J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39353858
-
Alteration of the Intra- and Inter-Lobe Connectivity of the Brain Structural Network in Normal Aging.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Jul 28;22(8):826. doi: 10.3390/e22080826. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33286597 Free PMC article.
-
Functional connectivity of the fusiform gyrus during a face-matching task in subjects with mild cognitive impairment.Brain. 2006 May;129(Pt 5):1113-24. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl051. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Brain. 2006. PMID: 16520329
-
Intra- and Inter-Modular Connectivity Alterations in the Brain Structural Network of Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3.Entropy (Basel). 2019 Mar 23;21(3):317. doi: 10.3390/e21030317. Entropy (Basel). 2019. PMID: 33267031 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

