SGC-CAMKK2-1: A Chemical Probe for CAMKK2
- PMID: 36672221
- PMCID: PMC9856672
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12020287
SGC-CAMKK2-1: A Chemical Probe for CAMKK2
Abstract
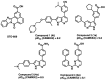
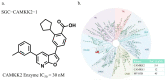
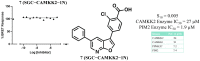
The serine/threonine protein kinase calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 (CAMKK2) plays critical roles in a range of biological processes. Despite its importance, only a handful of inhibitors of CAMKK2 have been disclosed. Having a selective small molecule tool to interrogate this kinase will help demonstrate that CAMKK2 inhibition can be therapeutically beneficial. Herein, we disclose SGC-CAMKK2-1, a selective chemical probe that targets CAMKK2.
Keywords: CAMKK2; NanoBRET; chemical probe; kinase; kinase selectivity.
Conflict of interest statement
D.E.F. has received research funding from GTx, Inc. and has familial relationships with Hummingbird Bioscience, Maia Biotechnology, Alms Therapeutics, Hinova Pharmaceuticals, and Barricade Therapeutics. The funders had no role in the conceptualization of the study or writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish this article. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
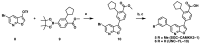
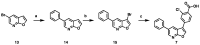
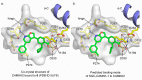

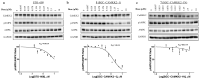
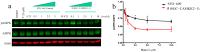
References
-
- Cary R.L., Waddell S., Racioppi L., Long F., Novack D.V., Voor M.J., Sankar U. Inhibition of Ca(2)(+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 stimulates osteoblast formation and inhibits osteoclast differentiation. J. Bone Min. Res. 2013;28:1599–1610. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1890. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williams J.N., Kambrath A.V., Patel R.B., Kang K.S., Mevel E., Li Y., Cheng Y.H., Pucylowski A.J., Hassert M.A., Voor M.J., et al. Inhibition of CaMKK2 Enhances Fracture Healing by Stimulating Indian Hedgehog Signaling and Accelerating Endochondral Ossification. J. Bone Min. Res. 2018;33:930–944. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Broxmeyer H.E., Ropa J., Capitano M.L., Cooper S., Racioppi L., Sankar U. CaMKK2 Knockout Bone Marrow Cells Collected/Processed in Low Oxygen (Physioxia) Suggests CaMKK2 as a Hematopoietic Stem to Progenitor Differentiation Fate Determinant. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022;18:2513–2521. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10306-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

