Erk1/2-Dependent HNSCC Cell Susceptibility to Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis
- PMID: 36672272
- PMCID: PMC9856753
- DOI: 10.3390/cells12020336
Erk1/2-Dependent HNSCC Cell Susceptibility to Erastin-Induced Ferroptosis
Abstract
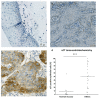
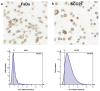
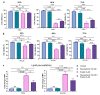
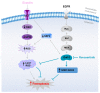
Unfavorable clinical outcomes mean that cancer researchers must attempt to develop novel therapeutic strategies to overcome therapeutic resistance in patients with HNSCC. Recently, ferroptosis was shown to be a promising pathway possessing druggable targets, such as xCT (SLC7A11). Unfortunately, little is known about the molecular mechanisms underlying the susceptibility of HNSCC cells to ferroptosis. The goal of this study was to determine whether HNSCC cells with activated Erk1/2 are vulnerable to ferroptosis induction. Our results have shown that xCT (SLC7A11) was overexpressed in malignant tissues obtained from the patients with HNSCC, whereas normal mucosa demonstrated weak expression of the protein. In order to investigate the role of Erk1/2 in the decrease in cell viability caused by erastin, xCT-overexpressing FaDu and SCC25 HNSCC cells were used. The ravoxertinib-dependent inhibition of Erk1/2 signaling led to the decrease in erastin efficacy due to the effect on ROS production and the upregulation of ROS scavengers SOD1 and SOD2, resulting in repressed lipid peroxidation. Therefore, it was concluded that the erastin-dependent activation of ferroptosis seems to be a promising approach which can be further developed as an additional strategy for the treatment of HNSCC. As ferroptosis induction via erastin is strongly dependent on the expression of Erk1/2, this MAP kinase can be considered as a predictor for cancer cells' response to erastin.
Keywords: ERK signaling; HNSCC; erastin; xCT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- De Angelis R., Sant M., Coleman M.P., Francisci S., Baili P., Pierannunzio D., Trama A., Visser O., Brenner H., Ardanaz E. Cancer survival in Europe 1999–2007 by country and age: Results of EUROCARE-5—A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:23–34. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70546-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

