Insights into Pathogenesis, Nutritional and Drug Approach in Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36672642
- PMCID: PMC9856128
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11010136
Insights into Pathogenesis, Nutritional and Drug Approach in Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review
Abstract
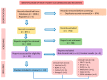
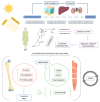
Sarcopenia is a multifactorial condition related to the loss of muscle mass and strength due to aging, eating habits, physical inactivity, or even caused by another disease. Affected individuals have a higher risk of falls and may be associated with heart disease, respiratory diseases, cognitive impairment, and consequently an increased risk of hospitalization, in addition to causing an economic impact due to the high cost of care during the stay in hospitals. The standardization of appropriate treatment for patients with sarcopenia that could help reduce pathology-related morbidity is necessary. For these reasons, this study aimed to perform a systematic review of the role of nutrition and drugs that could ameliorate the health and quality of life of sarcopenic patients and PRISMA guidelines were followed. Lifestyle interventions have shown a profound impact on sarcopenia treatment but using supplements and different drugs can also impact skeletal muscle maintenance. Creatine, leucine, branched-chain amino acids, omega 3, and vitamin D can show benefits. Although with controversial results, medications such as Metformin, GLP-1, losartan, statin, growth hormone, and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors have also been considered and can alter the sarcopenic's metabolic parameters, protect against cardiovascular diseases and outcomes, while protecting muscles.
Keywords: amino acids; drugs; inflammation; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

