The Molecular Pharmacology of Phloretin: Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Action
- PMID: 36672652
- PMCID: PMC9855955
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11010143
The Molecular Pharmacology of Phloretin: Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms of Action
Abstract
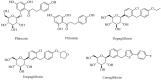
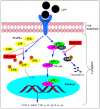
The isolation of phlorizin from the bark of an apple tree in 1835 led to a flurry of research on its inhibitory effect on glucose transporters in the intestine and kidney. Using phlorizin as a prototype drug, antidiabetic agents with more selective inhibitory activity towards glucose transport at the kidney have subsequently been developed. In contrast, its hydrolysis product in the body, phloretin, which is also found in the apple plant, has weak antidiabetic properties. Phloretin, however, displays a range of pharmacological effects including antibacterial, anticancer, and cellular and organ protective properties both in vitro and in vivo. In this communication, the molecular basis of its anti-inflammatory mechanisms that attribute to its pharmacological effects is scrutinised. These include inhibiting the signalling pathways of inflammatory mediators' expression that support its suppressive effect in immune cells overactivation, obesity-induced inflammation, arthritis, endothelial, myocardial, hepatic, renal and lung injury, and inflammation in the gut, skin, and nervous system, among others.
Keywords: COX; NF-κB; Nrf2; apple flavonoids; cytokines; iNOS; inflammation; phloretin; phlorizin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Picinelli A., Dapena E., Mangas J.J. Polyphenolic Pattern in apple tree leaves in relation to scab resistance. A preliminary study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995;43:2273–2278. doi: 10.1021/jf00056a057. - DOI
-
- Rieg T., Masuda T., Gerasimova M., Mayoux E., Platt K., Powell D.R., Thomson S.C., Koepsell H., Vallon V. Increase in SGLT1-mediated transport explains renal glucose reabsorption during genetic and pharmacological SGLT2 inhibition in euglycemia. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2014;306:F188–F193. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00518.2013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vrhovac I., Balen Eror D., Klessen D., Burger C., Breljak D., Kraus O., Radović N., Jadrijević S., Aleksic I., Walles T., et al. Localizations of Na(+)-D-glucose cotransporters SGLT1 and SGLT2 in human kidney and of SGLT1 in human small intestine, liver, lung, and heart. Pflugers Arch. 2015;467:1881–1898. doi: 10.1007/s00424-014-1619-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

