Molecular Characterization of Tropomyosin and Its Potential Involvement in Muscle Contraction in Pacific Abalone
- PMID: 36672743
- PMCID: PMC9858658
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14010002
Molecular Characterization of Tropomyosin and Its Potential Involvement in Muscle Contraction in Pacific Abalone
Abstract
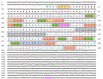
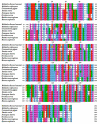
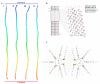
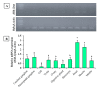
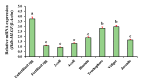
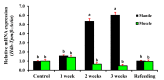
Tropomyosin (TPM) is a contractile protein responsible for muscle contraction through its actin-binding activity. The complete sequence of TPM in Haliotis discus hannai (Hdh-TPM) was 2160 bp, encoding 284 amino acids, and contained a TPM signature motif and a TPM domain. Gene ontology (GO) analysis based on the amino acid sequence predicted Hdh-TPM to have an actin-binding function in the cytoskeleton. The 3D analysis predicted the Hdh-TPM to have a coiled-coil α-helical structure. Phylogenetically, Hdh-TPM formed a cluster with other TPM/TPM1 proteins during analysis. The tissue-specific mRNA expression analysis found the higher expression of Hdh-TPM in the heart and muscles; however, during embryonic and larval development (ELD), the higher expression was found in the trochophore larvae and veliger larvae. Hdh-TPM expression was upregulated in fast-growing abalone. Increasing thermal stress over a long period decreased Hdh-TPM expression. Long-term starvation (>1 week) reduced the mRNA expression of Hdh-TPM in muscle; however, the mRNA expression of Hdh-TPM was significantly higher in the mantle, which may indicate overexpression. This study is the first comprehensive study to characterize the Hdh-TPM gene in Pacific abalone and to report the expression of Hdh-TPM in different organs, and during ELD, different growth patterns, thermal stress, seasonal changes, and starvation.
Keywords: cloning; coiled-coil structure; contractile function; expression analysis; gene ontology.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interests relevant to this study to disclose.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Neuropeptide HGAP Regulates Growth, Reproduction, Metamorphosis, Tissue Damage Repair, and Response against Starvation in Pacific Abalone.Neuroendocrinology. 2024;114(5):453-467. doi: 10.1159/000535945. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Neuroendocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38142675 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of Hdh-HSBP1 and its involvement in heat stress and early development in Pacific abalone, Haliotis discus hannai.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Aug;151:109660. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109660. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38830519
-
Molecular Characterization and Function of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 7 (BMP7) in the Pacific Abalone, Haliotis discus hannai.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 23;14(6):1128. doi: 10.3390/genes14061128. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372307 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Pathologies of Skeletal and Cardiac Muscles Caused by Point Mutations in the Tropomyosin Genes.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020 Jan;85(Suppl 1):S20-S33. doi: 10.1134/S0006297920140023. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2020. PMID: 32087052 Review.
-
Tropomyosin - master regulator of actin filament function in the cytoskeleton.J Cell Sci. 2015 Aug 15;128(16):2965-74. doi: 10.1242/jcs.172502. Epub 2015 Aug 3. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 26240174 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

