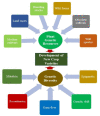
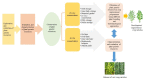
Genetic Diversity, Conservation, and Utilization of Plant Genetic Resources
- PMID: 36672915
- PMCID: PMC9859222
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14010174
Genetic Diversity, Conservation, and Utilization of Plant Genetic Resources
Abstract
Plant genetic resources (PGRs) are the total hereditary material, which includes all the alleles of various genes, present in a crop species and its wild relatives. They are a major resource that humans depend on to increase farming resilience and profit. Hence, the demand for genetic resources will increase as the world population increases. There is a need to conserve and maintain the genetic diversity of these valuable resources for sustainable food security. Due to environmental changes and genetic erosion, some valuable genetic resources have already become extinct. The landraces, wild relatives, wild species, genetic stock, advanced breeding material, and modern varieties are some of the important plant genetic resources. These diverse resources have contributed to maintaining sustainable biodiversity. New crop varieties with desirable traits have been developed using these resources. Novel genes/alleles linked to the trait of interest are transferred into the commercially cultivated varieties using biotechnological tools. Diversity should be maintained as a genetic resource for the sustainable development of new crop varieties. Additionally, advances in biotechnological tools, such as next-generation sequencing, molecular markers, in vitro culture technology, cryopreservation, and gene banks, help in the precise characterization and conservation of rare and endangered species. Genomic tools help in the identification of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) and novel genes in plants that can be transferred through marker-assisted selection and marker-assisted backcrossing breeding approaches. This article focuses on the recent development in maintaining the diversity of genetic resources, their conservation, and their sustainable utilization to secure global food security.
Keywords: crop improvement; ex situ conservation; genetic diversity; in situ conservation; plant genetic resources.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brown W.L. Genetic diversity and genetic vulnerability—An appraisal. Econ. Bot. 1983;37:4–12. doi: 10.1007/BF02859301. - DOI
-
- Nevo E., Beiles A., Ben-Shlomo R. The evolutionary significance of genetic diversity: Ecological, demographic and life history correlates. Lect. Notes Biomath. 1984;53:13–21.
-
- Hasan M., Abdullah H.M. Plant genetic resources and indigenous knowledge: An emerging needs for conservation. In: Salgotra R.K., Gupta B.B., editors. Plant Genetic Resources and Traditional Knowledge for Food Security. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2015. - DOI
-
- Ogwu M.C., Osawaru M.E., Ahana C.M. Challenges in conserving and utilizing plant genetic resources (PGR) Int. J. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2014;6:16–22. doi: 10.5897/IJGMB2013.0083. - DOI
-
- Ulukan H. Plant genetic resources and breeding: Current scenario and future prospects. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2011;13:447–454.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources