A Novel Deep Learning-Based Approach for Segmentation of Different Type Caries Lesions on Panoramic Radiographs
- PMID: 36673010
- PMCID: PMC9858411
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13020202
A Novel Deep Learning-Based Approach for Segmentation of Different Type Caries Lesions on Panoramic Radiographs
Abstract
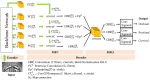
The study aims to evaluate the diagnostic performance of an artificial intelligence system based on deep learning for the segmentation of occlusal, proximal and cervical caries lesions on panoramic radiographs. The study included 504 anonymous panoramic radiographs obtained from the radiology archive of Inonu University Faculty of Dentistry's Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology from January 2018 to January 2020. This study proposes Dental Caries Detection Network (DCDNet) architecture for dental caries segmentation. The main difference between DCDNet and other segmentation architecture is that the last part of DCDNet contains a Multi-Predicted Output (MPO) structure. In MPO, the final feature map split into three different paths for detecting occlusal, proximal and cervical caries. Extensive experimental analyses were executed to analyze the DCDNet network architecture performance. In these comparison results, while the proposed model achieved an average F1-score of 62.79%, the highest average F1-score of 15.69% was achieved with the state-of-the-art segmentation models. These results show that the proposed artificial intelligence-based model can be one of the indispensable auxiliary tools of dentists in the diagnosis and treatment planning of carious lesions by enabling their detection in different locations with high success.
Keywords: caries diagnosis; convolutional neural network; deep learning; dental panoramic radiographs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kassebaum N.J., Smith A.G., Bernabé E., Fleming T.D., Reynolds A.E., Vos T., Murray C., Marcenes W., Collaborators G.O.H. Global, regional, and national prevalence, incidence, and disability-adjusted life years for oral conditions for 195 countries, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. J. Dent. Res. 2017;96:380–387. doi: 10.1177/0022034517693566. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keerthana S., Mohammed H., Hariprasad A., Anand M., Ayesha S. Comparative evaluation of condylar guidance obtained by three different interocclusal recording materials in a semi-adjustable articulator and digital panoramic radiographic images in dentate patients: An in vivo study. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2021;21:397. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

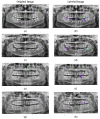
 Type I (Occlusal caries).
Type I (Occlusal caries).  Type II (Proximal caries).
Type II (Proximal caries).  Type III (Cervical caries).
Type III (Cervical caries).